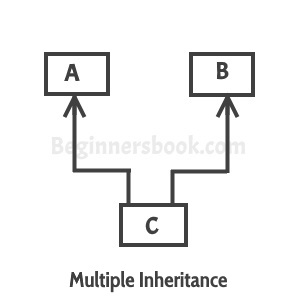
When one class extends more than one classes then this is called multiple inheritance. For example: Class C extends class A and B then this type of inheritance is known as multiple inheritance. Java doesn’t allow multiple inheritance. In this article, we will discuss why java doesn’t allow multiple inheritance and how we can use interfaces instead of classes to achieve the same purpose.
Why Java doesn’t support multiple inheritance?
C++ , Common lisp and few other languages supports multiple inheritance while java doesn’t support it. Java doesn’t allow multiple inheritance to avoid the ambiguity caused by it. One of the example of such problem is the diamond problem that occurs in multiple inheritance.
To understand the basics of inheritance, refer this main guide: Inheritance in Java
What is diamond problem?
We will discuss this problem with the help of the diagram below: which shows multiple inheritance as Class D extends both classes B & C. Now lets assume we have a method in class A and class B & C overrides that method in their own way. Wait!! here the problem comes – Because D is extending both B & C so if D wants to use the same method which method would be called (the overridden method of B or the overridden method of C). Ambiguity. That’s the main reason why Java doesn’t support multiple inheritance.
Can we implement more than one interfaces in a class
Yes, we can implement more than one interfaces in our program because that doesn’t cause any ambiguity(see the explanation below).
interface X
{
public void myMethod();
}
interface Y
{
public void myMethod();
}
class JavaExample implements X, Y
{
public void myMethod()
{
System.out.println("Implementing more than one interfaces");
}
public static void main(String args[]){
JavaExample obj = new JavaExample();
obj.myMethod();
}
}
Output:
Implementing more than one interfaces
As you can see that the class implemented two interfaces. A class can implement any number of interfaces. In this case there is no ambiguity even though both the interfaces are having same method. Why? Because methods in an interface are always abstract by default, which doesn’t let them give their implementation (or method definition ) in interface itself.
Sanjay says
Thanks, I have a question.
1. Why do we need interfaces anyway? Couldn’t we just declare and define myMethod() inside Demo class? I don’t see the point of multiple inheritance as both interfaces have empty abstract methods.
2. Can you give me a real example which we really need interfaces in real life.
3. Are there any real-world examples where we really need interfaces and things that we can’t accomplish without them?
Kaamakshi Sharma says
real life interface is also called abstraction because as in interface we only declare methods and variable not defining it any way .
consider that you r going from half day leave so in order to inform to your friends you will say that i m going to my home not describing that what you will do at home this is similar to your interface…
MONIS AZHAR says
We need interface because it gives order to must implement its requirements.
Example:
If you have 2 shops, one shop is required ISO-9000 certifiction then you’ll just inherit its class with ISO-9000 interface in order to fullfill their requirements. Where ISO-9000 interface contains all the requirements which one must have to implement before got certified.
That is why one class can inherit with multiple interfaces because your shop can have multiple certifications.
I hope now you’ll understand the use of interfaces.
Shashikumar says
I just have one question.
As a real time example can any one show us the use of interfaces to inherit all the features Class “Applet” & Class “Swing”.
anji says
I just have one question.
In above example Demo class myMethod function,Which interface has been utilized to override.
Joseph says
What if interface x and interface y’s methods have different return types? Apparently it’s legal because it’s not a part of the method signature. How would you deal with that?
Husoski says
It’s legal for two different interfaces to have methods with the same name and arguments, but different return types. However, if that’s the case, it’s impossible for any class to implement both interfaces.
muralidhar says
how can we say multiple inheritance supported in java at interface level. if we implement two or more interfaces into our class with same variables in all interfaces . I got error doing this. give me example.
Somnath Pagar says
Nice explanation.
I have question,
Some people says interface supports only syntax of multiple inheritance does not supports implementation of multiple inheritance
Is it true?if yes then how?
amrish yadav says
i have a 1 question how multiple inheritance is suspended in java please give me answer