The add() method of Java ArrayList class is used to add elements to an ArrayList. In this guide, we will see various examples of add method.
Syntax
1. To add element at the end of the list:
public boolean add (E element)
2. To add elements at a specific position:
public void add(int index, Object element)
Java ArrayList add Method Examples
Let’s see examples to understand how the add method works:
1. Adding element at the end of the list
This is the basic program, here we are just calling the add method to add new elements to the end of the ArrayList.
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> arrList = new ArrayList<>();
arrList.add("Ram"); // [Ram]
arrList.add("Steve"); // [Ram, Steve]
arrList.add("John"); // [Ram, Steve, John]
System.out.println(arrList);
}
}
Output:
[Ram, Steve, John]
2. Adding an element to the beginning of ArrayList
You can add the element to the beginning of ArrayList by calling add method like this: add(0, Element). ArrayList is based on zero based indexing, which means first element is present at the index 0. The other elements in the ArrayList are shifted, which means after adding new element to the front, the first element becomes second, second element becomes third and so on.
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> arrList = new ArrayList<>();
arrList.add("Ram"); // [Ram]
arrList.add("Steve"); // [Ram, Steve]
arrList.add("John"); // [Ram, Steve, John]
// instead of adding the element at the end, we are
// adding the element in the beginning using
// add(int index, Object element) method variation
arrList.add(0, "Chaitanya");
System.out.println(arrList);
}
}
Output:
[Chaitanya, Ram, Steve, John]
3. Add element in ArrayList if it doesn’t exist
For this example, we are using another ArrayList method contains(), which checks if the element already present in the arraylist or not. It returns true, if element exists else returns false.
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> arrList = new ArrayList<>();
arrList.add(1);
arrList.add(10);
arrList.add(5);
System.out.print("Enter an integer number: ");
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int temp = scan.nextInt();
//checking if element exists
//add element if doesn't exist
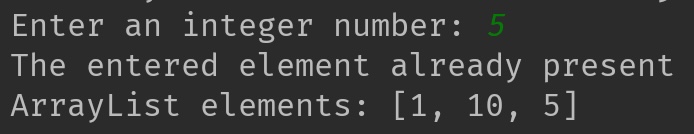
if(arrList.contains(temp)){
System.out.println("The entered element already present");
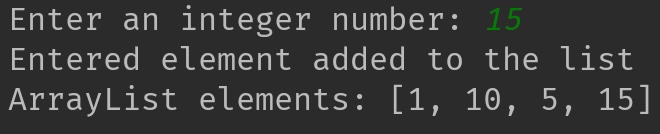
}else{
arrList.add(temp);
System.out.println("Entered element added to the list");
}
System.out.println("ArrayList elements: "+arrList);
}
}
Output 1: If user enters an element that already exists
Output 2: If user enters an element that doesn’t exist
4. Adding null values to ArrayList
In this example, we are adding null values to the ArrayList, which is perfectly fine. However if you only want to iterate non-null values then you can do it like this:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> arrList = new ArrayList<>();
arrList.add(1);
arrList.add(10);
arrList.add(5);
arrList.add(null); //adding null
System.out.println("ArrayList elements: "+arrList);
System.out.println("ArrayList not-null elements: ");
//if only want to print elements that are not null
for (Integer item : arrList) {
if (item != null)
System.out.println(item);
}
}
}
Output:
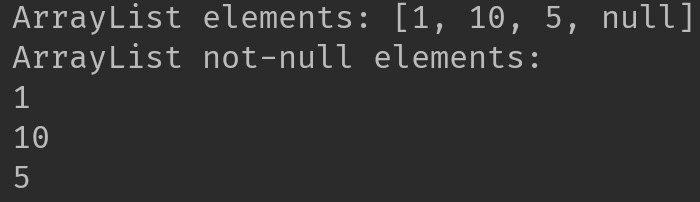
5. ArrayList IndexOutOfBoundsException
The reason the following program throws IndexOutOfBoundsException is: The ArrayList grows in size dynamically, you cannot add third element in the ArrayList without adding the second element, which is what we are trying to do in the following program.
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String[] args){
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(0, "Hi"); // ["Hi"]
list.add(0, "Hello");// ["Hello", "Hi"]
// throws IndexOutOfBoundsException
list.add(3, "Bye");
}
}
Output:
IndexOutOfBoundsException
Samira kumar Biswal says
In Collection Topics,please provide how all the collection classes and interfaces also Map classes and interfaces internally works and which algorithm it follws.