Switch case statement is used when we have number of options (or choices) and we may need to perform a different task for each choice.
The syntax of Switch case statement looks like this –
switch (variable or an integer expression)
{
case constant:
//Java code
;
case constant:
//Java code
;
default:
//Java code
;
}
Switch Case statement is mostly used with break statement even though it is optional. We will first see an example without break statement and then we will discuss switch case with break
A Simple Switch Case Example
public class SwitchCaseExample1 {
public static void main(String args[]){
int num=2;
switch(num+2)
{
case 1:
System.out.println("Case1: Value is: "+num);
case 2:
System.out.println("Case2: Value is: "+num);
case 3:
System.out.println("Case3: Value is: "+num);
default:
System.out.println("Default: Value is: "+num);
}
}
}
Output:
Default: Value is: 2
Explanation: In switch I gave an expression, you can give variable also. I gave num+2, where num value is 2 and after addition the expression resulted 4. Since there is no case defined with value 4 the default case got executed. This is why we should use default in switch case, so that if there is no catch that matches the condition, the default block gets executed.
Switch Case Flow Diagram
First the variable, value or expression which is provided in the switch parenthesis is evaluated and then based on the result, the corresponding case block is executed that matches the result.
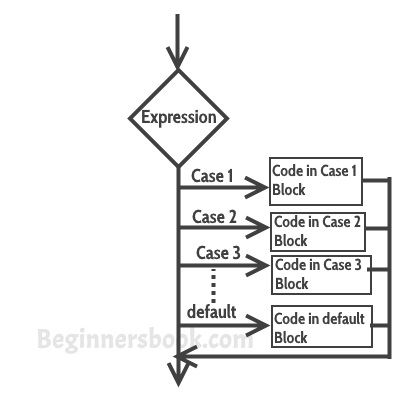
Break statement in Switch Case
Break statement is optional in switch case but you would use it almost every time you deal with switch case. Before we discuss about break statement, Let’s have a look at the example below where I am not using the break statement:
public class SwitchCaseExample2 {
public static void main(String args[]){
int i=2;
switch(i)
{
case 1:
System.out.println("Case1 ");
case 2:
System.out.println("Case2 ");
case 3:
System.out.println("Case3 ");
case 4:
System.out.println("Case4 ");
default:
System.out.println("Default ");
}
}
}
Output:
Case2 Case3 Case4 Default
In the above program, we have passed integer value 2 to the switch, so the control switched to the case 2, however we don’t have break statement after the case 2 that caused the flow to pass to the subsequent cases till the end. The solution to this problem is break statement
Break statements are used when you want your program-flow to come out of the switch body. Whenever a break statement is encountered in the switch body, the execution flow would directly come out of the switch, ignoring rest of the cases
Let’s take the same example but this time with break statement.
Example with break statement
public class SwitchCaseExample2 {
public static void main(String args[]){
int i=2;
switch(i)
{
case 1:
System.out.println("Case1 ");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("Case2 ");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("Case3 ");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("Case4 ");
break;
default:
System.out.println("Default ");
}
}
}
Output:
Case2
Now you can see that only case 2 had been executed, rest of the cases were ignored.
Why didn’t I use break statement after default?
The control would itself come out of the switch after default so I didn’t use it, however if you still want to use the break after default then you can use it, there is no harm in doing that.
Few points about Switch Case
1) Case doesn’t always need to have order 1, 2, 3 and so on. It can have any integer value after case keyword. Also, case doesn’t need to be in an ascending order always, you can specify them in any order based on the requirement.
2) You can also use characters in switch case. for example –
public class SwitchCaseExample2 {
public static void main(String args[]){
char ch='b';
switch(ch)
{
case 'd':
System.out.println("Case1 ");
break;
case 'b':
System.out.println("Case2 ");
break;
case 'x':
System.out.println("Case3 ");
break;
case 'y':
System.out.println("Case4 ");
break;
default:
System.out.println("Default ");
}
}
}
3) The expression given inside switch should result in a constant value otherwise it would not be valid.
For example:
Valid expressions for switch:
switch(1+2+23) switch(1*2+3%4)
Invalid switch expressions:
switch(ab+cd) switch(a+b+c)
4) Nesting of switch statements are allowed, which means you can have switch statements inside another switch. However nested switch statements should be avoided as it makes program more complex and less readable.
Check out these related java programs:
Leave a Reply