MongoDB is an open source, document oriented database that stores data in form of documents (key and value pairs). As discussed in our last tutorial (NoSQL introduction) that document based databases are one of types of NoSQL databases.
What is a document?
If you came from a relational database background then you can think of them as rows in RDBMS. The mapping between relational database and MongoDB is covered in the next tutorial so if you want to know the equivalent of rows, tables, columns in MongoDB, you should definitely check it: Mapping Relational database to MongoDB.
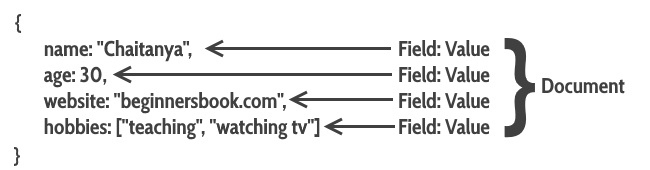
{
name: "Chaitanya",
age: 30,
website: "beginnersbook.com",
hobbies: ["Teaching", "Watching TV"]
}
This is a JSON like structure. Where data is stored in form of key and value pairs.
History of MongoDB
MongoDB was created by Eliot and Dwight (founders of DoubleClick) in 2007, when they faced scalability issues while working with relational database. The organization that developed MongoDB was originally known as 10gen.
In Feb 2009, they changed their business model and released MongoDB as an open source Project. The organization changed its name in 2013 and now known as MongoDB Inc.
Features of MongoDB
1. MongoDB provides high performance. Most of the operations in the MongoDB are faster compared to relational databases.
2. MongoDB provides auto replication feature that allows you to quickly recover data in case of a failure.
3. Horizontal scaling is possible in MongoDB because of sharing. Sharding is partitioning of data and placing it on multiple machines in such a way that the order of the data is preserved.
Horizontal scaling vs vertical scaling:
Vertical scaling means adding more resources to the existing machine while horizontal scaling means adding more machines to handle the data. Vertical scaling is not that easy to implement, on the other hand horizontal scaling is easy to implement. Horizontal scaling database examples: MongoDB, Cassandra etc.
4. Load balancing: Horizontal scaling allows MongoDB to balanace the load.
5. High Availabilty: Auto Replication improves the availability of MongoDB database.
6. Indexing: Index is a single field within the document. Indexes are used to quickly locate data without having to search every document in a MongoDB database. This improves the performance of operations performed on the MongoDB database.
Leave a Reply