In this guide, we will see how to work with numbers in Python. Python supports integers, floats and complex numbers.
An integer is a number without decimal point for example 5, 6, 10 etc.
A float is a number with decimal point for example 6.7, 6.0, 10.99 etc.
A complex number has a real and imaginary part for example 7+8j, 8+11j etc.
Example: Numbers in Python
# Python program to display numbers of # different data types # int num1 = 10 num2 = 100 print(num1+num2) # float a = 10.5 b = 8.9 print(a-b) # complex numbers x = 3 + 4j y = 9 + 8j print(y-x)
Output:
110 1.5999999999999996 (6+4j)
Python example to find the class(data type) of a number
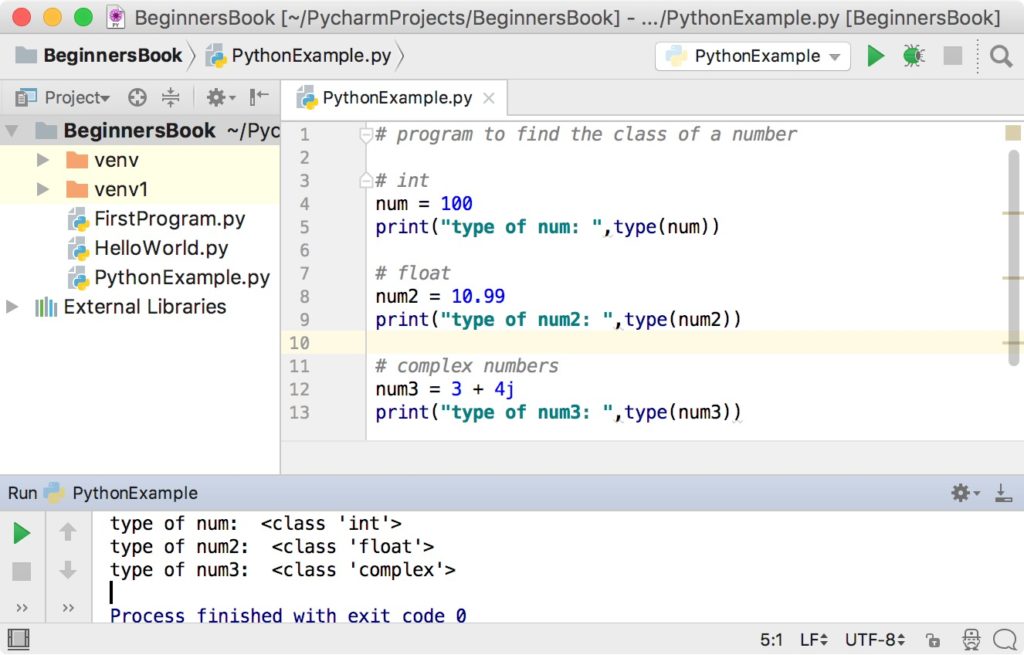
We can use the type() function to find out the class of a number. An integer number belongs to int class, a float number belongs to float class and a complex number belongs to complex class.
# program to find the class of a number
# int
num = 100
print("type of num: ",type(num))
# float
num2 = 10.99
print("type of num2: ",type(num2))
# complex numbers
num3 = 3 + 4j
print("type of num3: ",type(num3))
Output:
The isinstance() function
The isinstance() functions checks whether a number belongs to a particular class and returns true or false based on the result.
For example:
isinstance(num, int) will return true if the number num is an integer number.
isinstance(num, int) will return false if the number num is not an integer number.
Example of isinstance() function
num = 100 # true because num is an integer print(isinstance(num, int)) # false because num is not a float print(isinstance(num, float)) # false because num is not a complex number print(isinstance(num, complex))
Output:
True False False
Anu says
Hi Chaitanya, good job. I find your tutorial useful, crisp, to the point. Thank you!