In the previous tutorial we have seen the DBMS architecture – one-tier, two-tier and three-tier. In this guide, we will discuss the three level DBMS architecture in detail.
DBMS Three Level Architecture Diagram
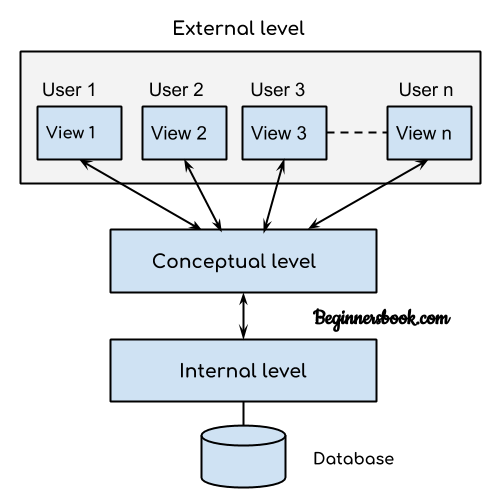
This architecture has three levels:
1. External level
2. Conceptual level
3. Internal level
1. External level
It is also called view level. The reason this level is called “view” is because several users can view their desired data from this level which is internally fetched from database with the help of conceptual and internal level mapping.
The user doesn’t need to know the database schema details such as data structure, table definition etc. user is only concerned about data which is what returned back to the view level after it has been fetched from database (present at the internal level).
External level is the “top level” of the Three Level DBMS Architecture.
2. Conceptual level
It is also called logical level. The whole design of the database such as relationship among data, schema of data etc. are described in this level.
Database constraints and security are also implemented in this level of architecture. This level is maintained by DBA (database administrator).
3. Internal level
This level is also known as physical level. This level describes how the data is actually stored in the storage devices. This level is also responsible for allocating space to the data. This is the lowest level of the architecture.
Leave a Reply