A function is a block of related statements that together perform a specific task. For example lets say we have to write three lines of code to find the average of two numbers, if we create a function to find the average then instead of writing those three lines again and again, we can just call the function we created.
Types of Function in Kotlin
There are two types of functions in Kotlin:
1. Standard Library Function
2. User-defined functions

1. Standard Library Function
The functions that are already present in the Kotlin standard library are called standard library functions or built-in functions or predefined functions. For example when we need to use the Math.floor() function we do not define the function because it is already present and we can directly call it in our code.
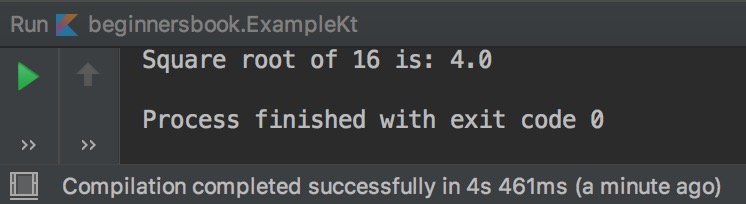
Standard Library Function Example
fun main(args : Array<String>){
var num = 16
println("Square root of $num is: ${Math.sqrt(num.toDouble())}")
}
Output:
2. User-defined functions
The functions that we define in our program before we call them are known as user defined functions. For example, lets say we want a function a check even or odd number in our program then we can create a function for this task and later call the function where we need to perform the check.
User-defined functions Example
We create a function using fun keyword. Lets create a function that prints “Hello”.
//Created the function
fun sayHello(){
println("Hello")
}
fun main(args : Array<String>){
//Calling the function
sayHello()
}
Output:
Hello
User defined function with arguments and return type
Syntax:
fun function_name(param1: data_type, param2: data_type, ...): return_type
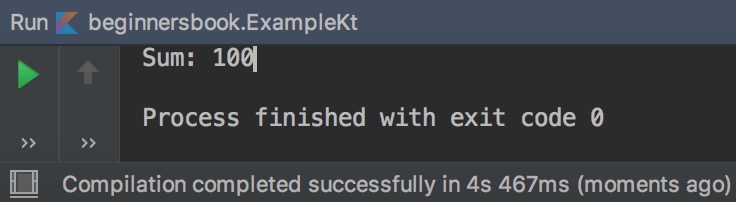
Lets create a user defined function that accepts the arguments and has a return type. In the following program we have declared a function sum. This function accepts variable number of arguments thats why we have used vararg, those arguments are of type integers and the return type of the function is also an integer.
//Created the function
fun sum(vararg numbers: Int): Int
{
var sum = 0
numbers.forEach {num -> sum += num}
return sum
}
fun main(args : Array<String>){
println("Sum: ${sum(10, 20, 30, 40)}")
}
Output:
Kotlin Inline functions
An inline function can be defined inside the main() function. Lets take an example of inline function. In the following example we have defined an inline function sum which accepts two integer arguments num1 and num2 and return type is integer.
fun main(args : Array<String>){
val sum = {num1: Int, num2: Int -> num1 + num2}
println("6 + 4 = ${sum(6,4)}")
}
Output:
6 + 4 = 10
Leave a Reply