In this guide, we will discuss the differences between Star and Bus Topologies.
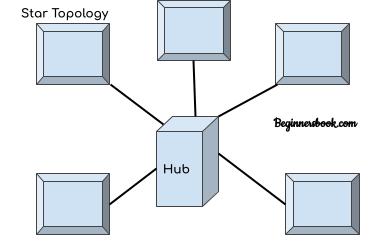
Star Topology:
In Star topology, n devices can be connected to a network using n number of links. Each device is connected to a central device known as hub. This hub acts as an intermediary between sender and receiver device. The sender device sends the data to the hub with the destination address. The hub receives the data and forwards it to the designated device.
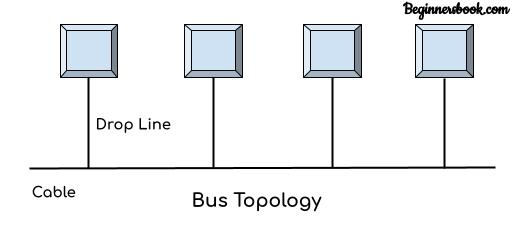
Bus Topology:
In Bus topology, all the devices are connected to a single cable (main cable or backbone) using the drop lines. The sender device transmits the data to the backbone cable. The data is available on the main cable and received by the designated device. There is however a limit of drop lines and the length a main cable can have.
Read topologies in detail: Types of Topologies
Difference between Star and Bus Topology
| Star Topology | Bus Topology |
|---|---|
| 1. In Star topology, all devices are connected to hub. | In bus topology, all devices are connected to a single cable known as backbone. |
| 2. Star topology doesn’t have a concept of terminator. | In bus topology, each end of the backbone cable has terminators. These terminators, removes the data from the backbone cable which is not received by any device. This is to free the bandwidth of the cable. |
| 3. Failure in the hub can cause the failure of entire network. | Failure or fault in the main cable (backbone) can bring the whole network down. |
| 4. Star topology is more expensive than bus topology. | Bus topology is less expensive compared to star topology. |
| 5. Star topology doesn’t have linear arrangement of devices in the network. | In bus topology, devices are arranged in a linear arrangement. |
| 6. Data transmission speed is high in star topology. | Data transmission speed is slower. |
| 7. Easily scalable. Adding new device to a star topology network is easy as the new device needs a connection to the central device hub. | Scalability is an issue as there is limit on number of devices. |
| 8. Data transmission is non-directional. | In bus topology, data transmission is uni-directional. |
| 9. Very low chance of data collision. When two or more devices send the data simultaneously then there is a chance of data collision. | High chance of data collision. |
| 10. Fault detection and troubleshooting is easier in star topology. | Fault detection is difficult in bus topology. |
| 11. In star topology, message from sender device is not broadcasted to all the devices in the network and only hub and receiver device get access to the data. | In bus topology, the message is broadcasted to all the devices in the network. |