A Star Topology is a network topology in which, devices are connected to a central device known as hub. This forms a star pattern thus this topology is named Star topology, it is also referred as star network. In this guide, we will discuss Star topology, its applications, types and advantages & disadvantages.
What is Star Topology?
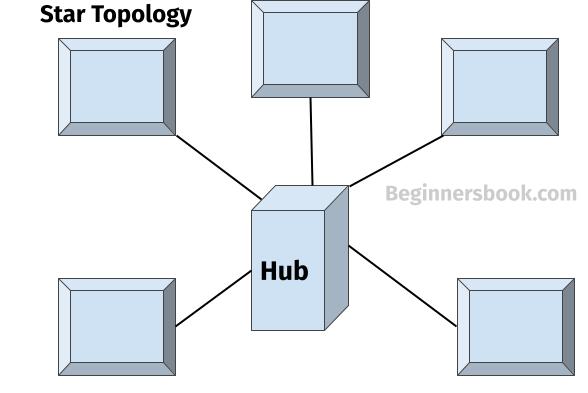
A computer network where each device is connected to a central device is known as star network or star topology.
Let’s discuss few details regarding star topology:
Client: The devices that are connected to the hub are called clients or peripheral devices.
Server: The central device (hub) acts as a server. Two devices cannot communicate directly, the sender device needs to send the data to hub first and then hub forwards the data to the receiver device.
Cable used: RJ-45 (Registered Jack – 45) Network cable and coaxial cable are the popular choices for star topology.
Limit: There is no limit on how many devices can be connected in the star topology, however the more device are connected, the slower is the network speed. This is because hub will be busy serving other devices requests while there are devices that are waiting for the current request to be finished.
Resetting of hub: If none of the device in the star network has access to the network resources then the reset switch is pressed, which resets the hub. When this resetting needs to be happened frequently, the hardware considered faulty and either replaced or a maintenance is performed based on the troubleshoot actions.
Read about all topologies: Computer Network Topology
Applications of Star Topology
The following are some of the real life applications of star topology:
- Bank: A bank has a server and all other computers are connected to the same server. All requests and communication happens through the server.
- Educational institution: Computer networks in educational institutions are generally connected using star topology. This is because usually there is a single server and all peripheral devices communicate through this server.
- Organizations: The big organizations also utilize this topology, their network is made up of multiple star networks where a group of devices are connected to a hub. There is a second hub for other group of devices and so on. This however is an example of hybrid topology.
Characteristics of Star Topology
A network in star topology has following characteristics:
- Star Topology is scalable as a new device just needs a connection to the hub, which can be easily implemented without affecting the other devices on the network.
- A peripheral device (client) failure doesn’t affect the whole network.
- There are n links required to connect n devices in the star network.
- More suitable for Local Area Network (LAN).
- Data transmission speed is fast and there is no chance of data collision as each device has one to one connection to hub, which means no bandwidth issue.
- Suitable for small sized network. This is because hub can handle a certain amount of load and more device will slowdown the entire network.
Star Topology Hardware Requirements
The hardware requirement is fully depend on the type of the network you are creating. For example, the type of cable required depends on the network card used in devices connected to the star network. Also, the cable is selected based on the length required to connect all the devices.
The speed of the network depends on the type of cable used and number of the devices in the network.
Types of Star Topology
As we learned in the beginning that devices in the star network does not communicate directly, rather they communicate via hub. There are three types of Star Topology based on the hub used in the network
- Passive Star Topology
- Active Star Topology
- Switch based Star Topology
1. Passive Star Topology
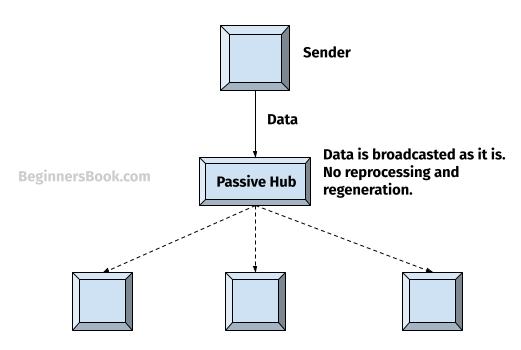
In Passive Star Topology, the hub is often called Passive hub. When a device wants to send data to another device on the network, it sends the data to passive hub.
The passive hub broadcasts the message (data) to all the devices connected to the network. The devices then perform the destination address check on the data.
If destination address matches with the device, the device keeps the data and other devices discard the data.
Pros:
- The advantage of this strategy is that the data can be passed to the destination without the intervention of hub.
- Minimal delay in data communication.
Cons:
- Not suitable for long length cables as the signal is weak.
- Passive hub doesn’t not regenerate or reprocess the signal so the signal strength is weak.
Suitable for: This type of star topology is suitable for small networks where data is not sensitive.
2. Active Star Topology
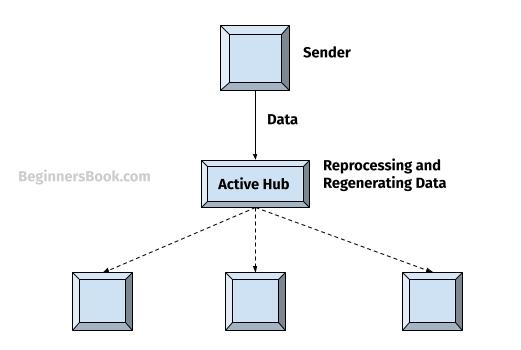
Unlike passive star topology, In active star topology, the active hub performs various operations on the received signal (data).
It can reprocess the received signal and can regenerate the signal to increase the strength of the signal.
Once the signal is regenerated, it works just like passive star topology and broadcasts the message to all the devices on the network.
Pros:
- Can work with big networks that are connected with lengthy cables.
- Signal strength is good.
Cons:
- Slight delay between sending and receiving the signal as additional measures taken by active hub.
3. Switch based Star Topology
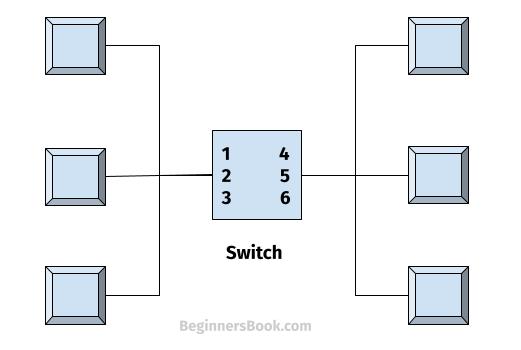
In switch based star topology, the central device hub is replaced with a smart device called switch. This switch can read the destination address on the received data. Once it detects the destination address, it creates a mapping table so that the incoming data frames can be transferred to the correct device.
Unlike passive and active star topology, switch does not broadcast the signal. It sends the signal to the intended receiver device only.
It also performs the following functions on the data:
- Routing: It detects the designated device and route the data to the intended device.
- Processing the signal: This is done to check the destination address so that the data can be routed to correct device.
- Network Management by switching multiple ports: Switch can simultaneously switch traffic between multiple ports so that the multiple devices can communicate simultaneously.
Advantages of Star Topology
1. Scalable
Star topology is scalable as a new device requires the connection with central unit (hub or switch). Other devices on the network are unaffected while the new device gets added to the network.
2. Easy Troubleshooting
It is easier to troubleshoot an issue in star topology as every device has a one to one connection with the hub. The faulty device can be detected and isolated without affecting other nodes.
3. Fast Speed
The speed of transmission is fast as the cable connecting the device and hub is a dedicated cable and only serves the data for the connected device.
4. Less Chances of data Collision
Data collision happens when multiple devices are sending the data on a shared channel at the same time. The chances of this happening in star topology is less as each device on the network has a dedicated link to the hub or switch.
Disadvantages of Star Topology
1. Hub Failure can bring entire network down
The central device is the backbone of the star network. The failure of the hub can bring down the whole network and can affect the communication of all the devices.
2. Cost is High
Cost of Star topology implementation is high as every device needs a dedicated cable connecting to hub, there are clients that do not communicate frequently, still they need the dedicated connection. The n devices on network needs n cables. This can increase the cost of setup.
3. Load on Central Unit
There is no way to handle the load on central unit. If number of devices attached are high then this can overload the hub quite a bit. This can hamper the performance of the network.
4. Number of cables required are high
In star topology, the number of cables required are more compared to other computer network topologies.
Extended Star Topology
An extended star topology is a combination of multiple star topologies. In Extended Star topology, several switches are connected to a switch to connect multiple star networks.
This is used in large organizations and universities. In Extended Star, the peripheral device sends message to the central hub or switch and then that switch sends the data to the main switch.

For example, in the above diagram, if top left device wants to communicate to the far bottom right device then:
- Sender sends the data to Switch1, the switch process the data and then send it to main Switch (Switch5).
- Switch5 reads the destination address and detects that the data needs to be sent to Switch4 as the destination device is directly connected to Switch4.
- When Switch4 receives the data, it process the data and then broadcasts to all the devices connected to it.
- The receiver device accept the data and other devices ignore it.
FAQ
Switch. A switch is used to join multiple devices to the network to create a physical star topology.
An extended star topology is created by joining multiple star topology networks. The switch of these star networks are connected to a main switch that maintains the connection between these multiple star topology networks.
Star topology is the most common network topology used in modern days. It is easy to implement, cost effective and easy to troubleshoot.