The bitCount() method of Java Integer class returns the number of 1’s bits in the two’s complement representation of the given integer value.
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i = 24;
// binary equivalent of 24 is: 11000
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(i));
System.out.println(Integer.bitCount(i));
}
}
Output:
11000 2
Syntax of bitCount() method
public static int bitCount(int i)
bitCount() Parameters
- i: An integer number
bitCount() Return Value
- The
bitCount()method has int return type. It returns the number of 1’s bits in the two’s complement representation of the given integer number. This process of counting 1’s in a binary number is also known as population count.
Example 1
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i = 50;
// binary equivalent of 50 is: 110010
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(i));
System.out.println(Integer.bitCount(i));
}
}
Output:
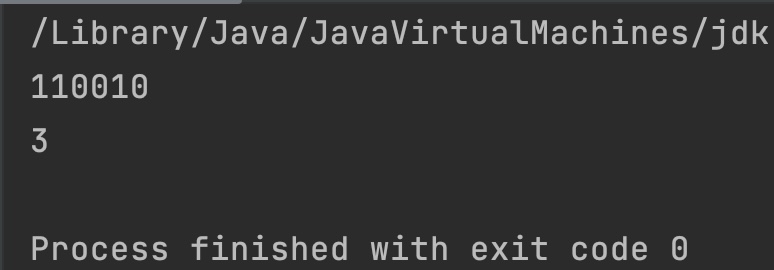
Example 2
import java.util.Scanner;
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i;
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
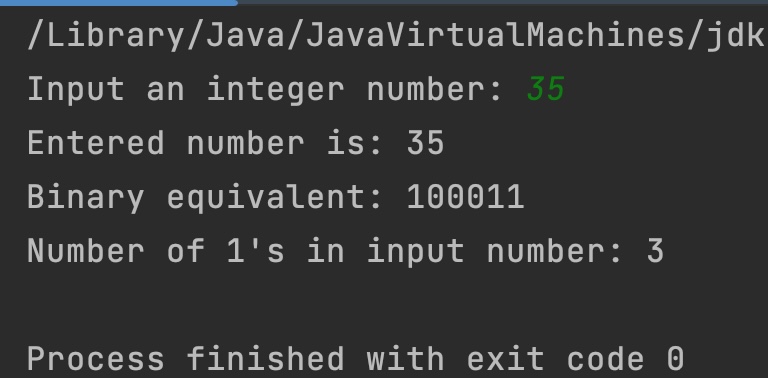
System.out.print("Input an integer number: " );
i = scan.nextInt();
System.out.println("Entered number is: "+i);
// Entered number binary conversion
System.out.println("Binary equivalent: "+
Integer.toBinaryString(i));
// Print 1's count
System.out.println("Number of 1's in input number: "+
Integer.bitCount(i));
}
}
Output:
Example 3
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String args[])
{
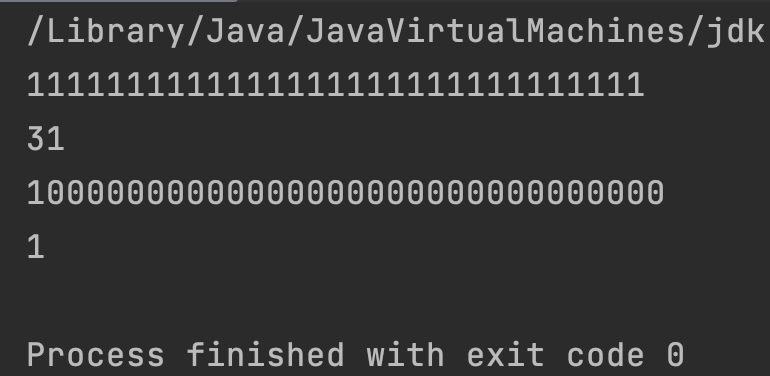
int i = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int i2 = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(i));
System.out.println(Integer.bitCount(i));
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(i2));
System.out.println(Integer.bitCount(i2));
}
}
Output: