Servlet Container creates ServletConfig object for each Servlet during initialization, to pass information to the Servlet. This object can be used to get configuration information such as parameter name and values from deployment descriptor file(web.xml).
Methods of ServletConfig interface
public String getInitParameter(String name): Returns the value of given parameter as String, or null if the given parameter doesn’t exist in web.xml.
public Enumeration getInitParameterNames(): Returns an enumeration of all the parameter names.
public String getServletName(): Returns the name of the servlet instance.
public ServletContext getServletContext(): Returns an object of ServletContext.
Example:
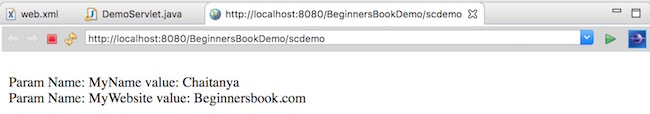
In this example, we will use two methods getInitParameter() and getInitParameterNames() to get all the parameters from web.xml along with their values.
The getInitParameterNames() method returns an enumeration of all parameters names and by passing those names during the call of getInitParameter() method, we can get the corresponding parameter value from web.xml.
DemoServlet.java
import java.io.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import java.util.Enumeration;
public class DemoServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
PrintWriter pwriter = response.getWriter();
ServletConfig sc=getServletConfig();
Enumeration<String> e=sc.getInitParameterNames();
String str;
while(e.hasMoreElements()) {
str=e.nextElement();
pwriter.println("<br>Param Name: "+str);
pwriter.println(" value: "+sc.getInitParameter(str));
}
}
}
web.xml
<web-app> <display-name>BeginnersBookDemo</display-name> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> <servlet> <servlet-name>MyServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>DemoServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>MyName</param-name> <param-value>Chaitanya</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>MyWebsite</param-name> <param-value>Beginnersbook.com</param-value> </init-param> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>MyServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/scdemo</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
Output:
Leave a Reply