The Java Collections Framework is a collection of interfaces and classes, which helps in storing and processing the data efficiently. This framework has several useful classes which have tons of useful functions which makes a programmer task super easy. I have written several tutorials on Collections in Java. All the tutorials are shared with examples and source codes to help you understand better.
Collections Framework hierarchy
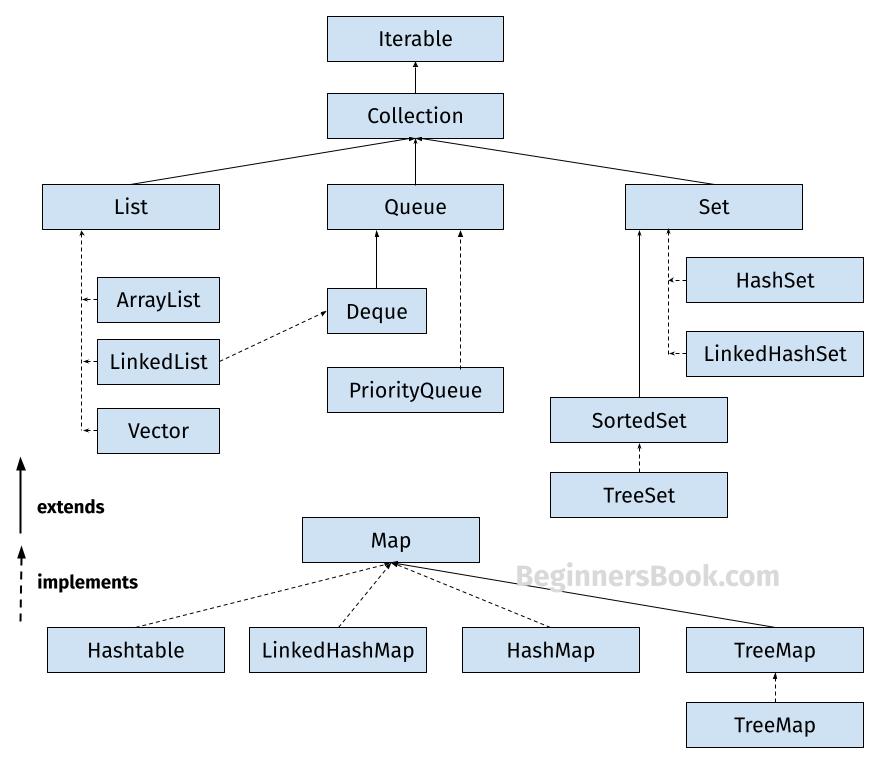
1. List
A List is an ordered Collection (sometimes called a sequence). Lists may contain duplicate elements. Elements can be inserted or accessed by their position in the list, using a zero-based index. The classes that implements List interface are:
- ArrayList
- LinkedList
- Vector
- Stack
1.1 ArrayList
ArrayList is a popular alternative of arrays in Java. It is based on an Array data structure. ArrayList is a resizable-array implementation of the List interface. It implements all optional list operations, and permits all elements, including null. Refer this guide to learn ArrayList in detail.
import java.util.*;
class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
//creating ArrayList of string type
ArrayList<String> arrList=new ArrayList<>();
//adding few elements
arrList.add("Cricket"); //list: ["Cricket"]
arrList.add("Hockey"); //list: ["Cricket", "Hockey"]
//inserting element at first position, index 0
//represents first element because ArrayList is based
//on zero based indexing system
arrList.add(0, "BasketBall"); //list: ["BasketBall", "Cricket", "Hockey"]
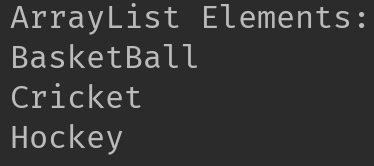
System.out.println("ArrayList Elements: ");
//Traversing ArrayList using enhanced for loop
for(String str:arrList)
System.out.println(str);
}
}
Output:
Refer the following guides to learn More about ArrayList:
Refer this collection, which contains all the articles related to ArrayList published on this website. It is regularly updated whenever a new article on ArrayList topic is published on this site.
1.2 LinkedList
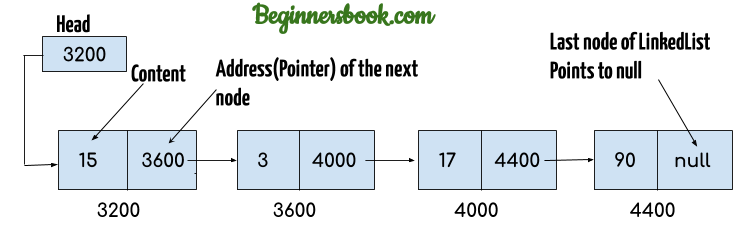
LinkedList is a linear data structure. However LinkedList elements are not stored in contiguous locations like arrays, they are linked with each other using pointers. Each element of the LinkedList has the reference(address/pointer) to the next element of the LinkedList.
import java.util.*;
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
LinkedList<String> linkList=new LinkedList<>();
linkList.add("Apple"); //["Apple"]
linkList.add("Orange"); //["Apple", "Orange"]
//inserting element at first position
linkList.add(0, "Banana"); ////["Banana", "Apple", "Orange"]
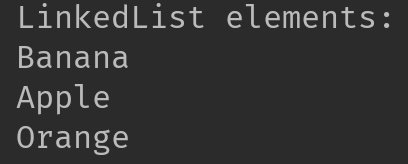
System.out.println("LinkedList elements: ");
//iterating LinkedList using iterator
Iterator<String> it=linkList.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}
Output:
Refer these article to learn More about LinkedList:
- LinkedList in Java
- How to iterate LinkedList
- Add element at the beginning and end of LinkedList
- Search element in LinkedList
- Convert LinkedList to ArrayList
Refer this collection, which contains all the articles related to LinkedList published on this website.
1.3 Vector
Here is the list of all the tutorials published on the Vector.
import java.util.*;
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
Vector<String> v=new Vector<>();
v.add("item1"); //["item1"]
v.add("item2"); //["item1", "item2"]
v.add("item3"); //["item1", "item2", "item3"]
//removing an element
v.remove("item2"); //["item1", "item3"]
System.out.println("Vector Elements: ");
//iterating Vector using iterator
Iterator<String> it=v.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}
Output:
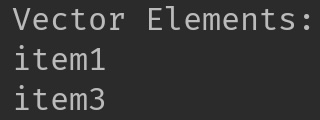
Refer this article for more guides on Vector.
1.4 Stack
Stack class extends Vector class, which means it is a subclass of Vector. Stack works on the concept of Last In First Out (LIFO). The elements are inserted using push() method at the end of the stack, the pop() method removes the element which was inserted last in the Stack.
import java.util.*;
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
//push() method adds the element in the stack
//and pop() method removes the element from the stack
stack.push("Chaitanya"); //["Chaitanya"]
stack.push("Ajeet"); //["Chaitanya", Ajeet]
stack.push("Hari"); //["Chaitanya", "Ajeet", "Hari"]
stack.pop(); //removes the last element
stack.push("Steve"); //["Chaitanya", "Ajeet", "Steve"]
stack.push("Carl"); //["Chaitanya", "Ajeet", "Steve", "Carl"]
stack.pop(); //removes the last element
System.out.println("Stack elements: ");
for(String str: stack){
System.out.println(str);
}
}
}
Output:

2. Set
A Set is a Collection that cannot contain duplicate elements. There are three main implementations of Set interface: HashSet, TreeSet, and LinkedHashSet.
2.1 HashSet
HashSet which stores its elements in a hash table, is the best-performing implementation. HashSet allows only unique elements. It doesn’t maintain the insertion order which means element inserted last can appear at first when traversing the HashSet.
import java.util.*;
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
HashSet<String> set=new HashSet<>();
set.add("Paul");
set.add("Ram");
set.add("Aaron");
set.add("Leo");
set.add("Becky");
Iterator<String> it=set.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}
Output:
Aaron Leo Paul Ram Becky
2.2 LinkedHashSet
Unlike HashSet, the LinkedHashSet maintains insertion order.
import java.util.*;
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
LinkedHashSet<String> set=new LinkedHashSet<>();
set.add("Paul");
set.add("Ram");
set.add("Aaron");
set.add("Leo");
set.add("Becky");
Iterator<String> it=set.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}
Output:
Paul Ram Aaron Leo Becky
2.3 TreeSet
TreeSet stores elements in a red-black tree. It is substantially slower than HashSet. TreeSet class implements SortedSet interface, which allows TreeSet to order its elements based on their values, which means TreeSet elements are sorted in ascending order.
import java.util.*;
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
TreeSet<String> set=new TreeSet<>();
set.add("Paul");
set.add("Ram");
set.add("Aaron");
set.add("Leo");
set.add("Becky");
Iterator<String> it=set.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}
Output:
Aaron Becky Leo Paul Ram
3. Map
A Map is an object that maps keys to values. A map cannot contain duplicate keys. There are three main implementations of Map interfaces: HashMap, TreeMap, and LinkedHashMap.
3.1 HashMap
HashMap: HashMap is like HashSet, it doesn’t maintain insertion order and doesn’t sort the elements in any order. Refer this guide to learn HashMap in detail.
import java.util.*;
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
HashMap<Integer, String> hmap = new HashMap<>();
//key and value pairs
hmap.put(101, "Chaitanya");
hmap.put(105, "Derick");
hmap.put(111, "Logan");
hmap.put(120, "Paul");
//print HashMap elements
Set set = hmap.entrySet();
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry)iterator.next();
System.out.print("key is: "+ m.getKey() + " & Value is: ");
System.out.println(m.getValue());
}
}
}
Output:
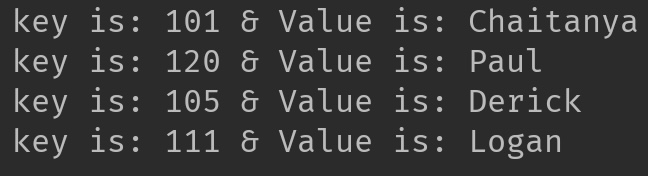
3.2 TreeMap
TreeMap: It stores its elements in a red-black tree. The elements of TreeMap are sorted in ascending order. It is substantially slower than HashMap. Refer this guide to learn TreeMap with examples.
This is the same example that we have seen above in HashMap. Here, elements are sorted based on keys.
import java.util.*;
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
TreeMap<Integer, String> hmap = new TreeMap<>();
//key and value pairs
hmap.put(101, "Chaitanya");
hmap.put(105, "Derick");
hmap.put(111, "Logan");
hmap.put(120, "Paul");
//print HashMap elements
Set set = hmap.entrySet();
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry)iterator.next();
System.out.print("key is: "+ m.getKey() + " & Value is: ");
System.out.println(m.getValue());
}
}
}
Output:
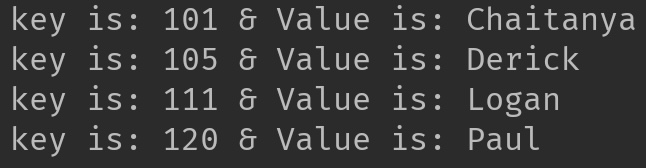
3.3 LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap: It maintains insertion order. Refer this guide, to learn LinkedHashMap in detail. As you can see: In the following example, the key & value pairs maintained the insertion order.
import java.util.*;
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
LinkedHashMap<Integer, String> hmap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
//key and value pairs
hmap.put(100, "Chaitanya");
hmap.put(120, "Paul");
hmap.put(105, "Derick");
hmap.put(111, "Logan");
//print LinkedHashMap elements
Set set = hmap.entrySet();
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry)iterator.next();
System.out.print("key is: "+ m.getKey() + " & Value is: ");
System.out.println(m.getValue());
}
}
}
Output:
key is: 100 & Value is: Chaitanya key is: 120 & Value is: Paul key is: 105 & Value is: Derick key is: 111 & Value is: Logan
More Tutorials on Collections in Java
To check all the tutorials (200+ guides) related to collections, published on this site: Refer this archive.
veeru says
Hi Sir,
I thank you very much for posting such an awesome java content.
The way you explained the Concepts are very clear.
But I am not able to find topics on List and Set.
Could you please let me know the link for accessing the List and set related topics ?
Rgds,
Manvi
Chaitanya Singh says
Thank you for your kind words. I have updated the page by providing links of List and Set related tutorials, you can find the same above.
sravani says
Hi sir,
This site is simply awesome.Thanks for your efforts.
we need more concepts from you like struts,hibernate ….!
Sundar says
Hai Sir,
This site is very useful for learners.I had one doubt, the doubt is, in hashmap and array concept we will display line and bar graph in one page with data input and cluster in JSP.what is the source code .Kindly tell me.Please send source code in my mail.
Thank you.
Ror says
This site helps me a lot.
avinash singh says
it is very easy program .i have understood and you will understand
sriram says
Hi Chaitanya,
Your content,depth of knowledge in the concepts is simply superb,mind blowing and awesome,i have visited many blogs and sites to learn the concepts in a easily understandable way, but i didn’t find any, but when i came across your site accidentally, i was amazed by way you make readers understand the concepts.
All these years i was feared of looking at the concepts of collections even,but now, after going through your site. That fear in me no more exist!!!! I thanks you from my bottom of heart for your kind knowledge sharing.
Regards,
Sriram.
Kalkidan Ferede says
I was looking for this kind of organized concept based tutorial on the Internet for an hour. indeed I succeeded! thank you sir! do you also have tutorials on JSF, hibernate, EJP, JPA, Spring, struts ? I really need to learn this topics from you if it is available. keep the good work!
Kalkidan Ferede says
Awsome! can you add why we need Iterator? why can’t we use loops(for loop, while loop, do while)?
Jitendra Gupta says
Hi kalkidan,
Iterator is used to iterate the element in one direction.
It’s having three method.
1. boolean hasNext( )
2. Object next( )
3. void remove( )
The best example you can use Iterator is
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(object1)
list.add(object2);
Iterator it = list.iterator();
while(it.hasNext() ){
Object obj = (Object)it.next();
}
Navin Israni says
Not all Collections provide index-based access, so we cannot always use while and do-while. There is an enhanced version of ‘for’ that can be used without index access.
In cases, where there is no index based access (i.e. set), we use an Iterator, otherwise it use your choice to choose the iteration method if the index is available to you.
uvi says
Great work buddy !!!!
I learned lot of thing from your site. Your explanations are very simple and clear.
keep it up.
best of luck !!!
Junaidali says
Good One Sir…
Pavan says
Hello Chaitanya, this tutorial is awesome. Many thanks for your efforts. Do we option to post our java queries in this site? If Yes, please let me know. If not, I think it would be a great enhancement for this site.
Srinivas says
Just one word..Brilliant tutorials.You helped me remove my fear over collections. I am thankful to you very much
Keep posting more tutorials
Murali.Bojanki says
Hi Sir,
the way your explanation is very very good, Beginners book is exactly suitable word for people who are learning new technology this website is 100% perfect for learners
Harish Patil says
Awesome explanation!!!!!
Thanks for such a simple and deep explanation of all concepts with example
Mirza Adil says
Nice Material
Fernando says
The content is very simple but yet very strong in communicating the concepts. Excellent set of tutorials.
Thanks a lot!!
Deepmala says
Hi Chaitanya!
Very good job.One of the best collections examples I have seen till date.Keep up the good work.All the best for all your future endeavors!
gyana ranajn says
where is hashtable ?
Rajapriya says
Hi Chaitanya
The explanations are simple and clear.I have learnt alot.
Thanks for your efforts!!
chandu says
I need collection programs in java with all interfaces and classes
Sairamsanthoshkumar M says
Hi,
Kindly suggest whether Vector comes under List interface???
I thought it was a legacy class.
Arvind Katte says
Absolutely awesome site for beginner…..
Most of java interview will ask question on JAVA COLLECTION FRAMEWORK,,, this site helps me lot…. thank you very much….
Swapnil Bijwe says
Really awesome site……each and every concept explained with very easy and simple example .for me you made collection is very easy.
Thank you so much for your efforts :)
Athul Shyam says
By far, this is the best website that I found easy for learning the concepts in Java. All the concepts are explained in a manner that it’s can be grasped quite easily. The topics seem to be very clear.
THANK YOU!! I’ll definitely recommend this site to my friends.
Chenna Harish says
superb…explanation with perfect matching examples. This is the best blog forever for COLLECTIONS concepts compare to others……..
Kiran S says
This site is really awesome. Now my all concepts are cleared regarding the Collections. It would be awesome if you provide tutorial for Spring, Struts and Hibernate too.
vijay says
nice one … very clear and time saving tutorial.. !!!
Abrutzi says
That’s really good job.Well done.Everything has been expained very clear and the examples has wrapped your theoritical parts in a great way.A good tutorial not only for beginners.Carry on the good job.
vittal says
In collection framework we have a class called “Stack”, i didn’t find it in diagram can you explain about this.
Pugal says
Hi bro your site really good particularly in collection section. Previously I dont known about collection but after saw your site I learnt collections part from your site. It was very much helpful to me. The same way I expecting Spring, SpringMVC, Hibernate from you.
kamalakannan.m says
hello sir …
this tutorial very help full to me . and want to learn spring framework
if you know please tell me or any good spring reference link send to my mail…
thankyou sir….
Rohan says
I just started learning Java . The Problem I faced initially was too many content in the internet. But your example seems to be one stop shop where I can get everything at one place. Keep Uploading the new topics in similar way. Just a advise , why dont you start Youtube channel ,you can explain theoretical concepts also :)
Sharan says
Thanks a lot for such an easy to understand programs and examples.Hats off to you.
priyanka says
Really awsome material and please add hibernate,struts2,springs and ajax.
Lib29 says
Thank You for giving a clear & precise understanding of Collections Framework. You have literally removed my fear of Collections. Keep up the Good Work. Thanks once again from the bottom of my heart!!!:)
Brent Grigsby says
Probably your best source for information on the Stack class is Oracle.com for the version of Java you are using. It will act similar to the other collection classes described here.
P.S. Nice job of explaining collection classes. I really like ArrayList because it dynamically grows as elements are added, eliminating array out of bounds exceptions. Thanks, Brent
sukirti shukla says
Sir i really like ur site and its content, everything is very organized and detailed, every topic is being covered with fine details. for a beginner this site is very useful,i request u sir to please introduce such type matter for data structure also.please
kavitha says
hi sir
your site is simply superb and easy to learn java! especially collections are very easy to understand and examples are really awesome! compared to other
sites this one is very nice and easy to learn! :)
Alekh Nema says
if collection is an interface and list also being an interface then..what i understand is list implements collection …but i also know that interface cannot implement another interface…than what is the justification for this?
aditya patel says
List is interface .
Collection is interface .
one interface always extends another interface .
so List extends Collection
Mary says
Thank you SO much! Literally saved me from failing my midterm.
Suni says
Awesome material!!!
Riya says
is map an object or interface?
vignesh says
map is a interface…
Swetha says
Hi ,
Hash Map can contain duplicate key values. Please correct it.
Great Job !! The Beginner’s book is one of the best sources to learn and make concepts clear.Thank you very much for your efforts.
Swetha.
Navin Prakash Israni says
HashMap can contain only one null key (and that key cannot have any value, because you can’t access the null key!). So having a null key as good as useless.
Rohit says
Hi,
This is awesome site :) the way you have explained all concepts are amazing…tysm
Preeti says
hello….sir
your tutorial is nice,can you tell me where is the use of collection in project and how?
Onur says
You are the best :) thanks for this tutorials
Rasika says
Hi Chaitanya, this beginners book has helped me a lot to grasp java concepts so easily. Your passion for java is making way for lots to understand these vast/complex java concepts more easily. You have structured tutorials for each and every topics soo nicely that only after reading this we can get clear understanding of each and every topic to implement them in practice. Thanks a lot for putting your passion into internet where it is helping us to grow our career.
vignesh says
It is nice..can we use arraylist inside hashmap?
Uma Shankar Gupta says
Hello All,
Could you please provide me link to follow the Spring Framework tutorials.
Thanks and Regards,
Uma Shankar Gupta
uday says
Hai Chaitanya,
Iam a HardCore fan of this Beginners Book . I would like to know about Colletion in depth. Queue Interface and some of the concepts are not provided.Could you please Provide all Collection Topics.
Thanks&Regards
Uday Kumar Mashetti.
Priya Muruganantham says
Hi Chitanya,
Awesome explanation on collections…looking forward for explanations about ConcurrentHashMaps,etc thru you.
Thanks
Priya M
Rajnayan says
Hello Chaitanya,
You have not provided tutorials for “HASHTABLE”.
Could you please provide the same?
Regards,
Rajnayan
Manan says
Hi Chaitanya,
Please correct this – TreeMap: It stores its elements in a red-black tree, orders its elements based on their VALUES.
It should be “orders its elements based on their KEYS”
Excellent article, thanks a ton!
Niloy says
Add hastable to the content and we are done. Great work though! :)
Harish Kashyap says
HI Chaitanya
You did a brilliant job on Beginnersbook’s Collection Framework. I appreciate you for such a best study content.
Thank you Sir.
Ramesh says
why we need listIterator can you please explain?
Paramasivam says
Hi, This site contents are very clear and given neat explanation about collection framework. As a beginner, This site could be very useful. thank you for your effort to making this blog and it will be very helpful us to learn about collection. We were expecting more updates on collection framework.
Thank you!..
VK says
Best online site….but in collections chapter Queue Interface is missing…plz upload it also…thanks