An array is a collection of similar items stored in contiguous memory locations. In programming, sometimes a simple variable is not enough to hold all the data. For example, lets say we want to store the marks of 500 students, having 500 different variables for this task is not feasible, we can define an array with size 500 that can hold the marks of all students.
Declaring an array in C++
There are couple of ways to declare an array.
Method 1:
int arr[5]; arr[0] = 10; arr[1] = 20; arr[2] = 30; arr[3] = 40; arr[4] = 50;
Method 2:
int arr[] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
Method 3:
int arr[5] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
Accessing Array Elements
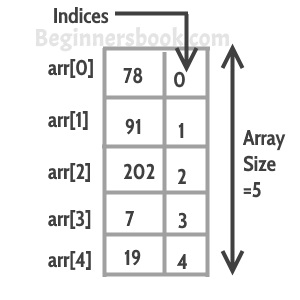
Array index starts with 0, which means the first array element is at index 0, second is at index 1 and so on. We can use this information to display the array elements. See the code below:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int arr[] = {11, 22, 33, 44, 55};
cout<<arr[0]<<endl;
cout<<arr[1]<<endl;
cout<<arr[2]<<endl;
cout<<arr[3]<<endl;
cout<<arr[4]<<endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
11 22 33 44 55
Although this code worked fine, displaying all the elements of array like this is not recommended. When you want to access a particular array element then this is fine but if you want to display all the elements then you should use a loop like this:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int arr[] = {11, 22, 33, 44, 55};
int n=0;
while(n<=4){
cout<<arr[n]<<endl;
n++;
}
return 0;
}
Leave a Reply