We have already learned that Java 8 introduced the Stream API along with several other cool features. If you are not familiar with Streams then refer this guide: Java 8 – Stream API. Java 9 introduced four new methods for Stream API. These methods are added in java.util.Stream interface.
Java 9 – Stream API Improvements
Java 9 added the following four methods to the Stream. Since Stream is an interface, the methods added to it are default and static. This is because java 8 allows us to have default and static methods in interface.
1. dropWhile() – default method
2. takeWhile() – default method
3. iterate() – static method
4. ofNullable() – static method
Java 9 – Stream dropWhile() method
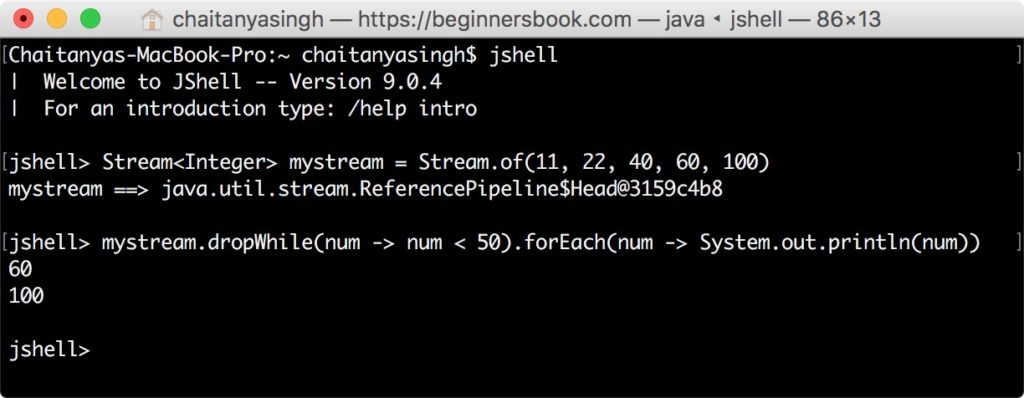
The method dropWhile() drops all the elements of the stream until the given predicate fails.
For example:
jshell> Stream<Integer> mystream = Stream.of(11, 22, 40, 60, 100) mystream ==> java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head@3159c4b8 jshell> mystream.dropWhile(num -> num < 50).forEach(num -> System.out.println(num)) 60 100
Note: When the stream is unordered, the dropWhile() drops all the elements until the given predicate fails, this method does not check further elements of the stream once the predicate fails. This means that the resulted stream may have elements that matches the predicate, lets take an example to understand this.
jshell> Stream<Integer> mystream = Stream.of(11, 22, 40, 60, 10, 15, 30, 100) mystream ==> java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head@3159c4b8 jshell> mystream.dropWhile(num -> num < 50).forEach(num -> System.out.println(num)) 60 10 15 30 100
Here the elements 10, 15, 30 that are present in the stream after element 60, matches the predicate but they were not dropped by dropWhile() because when the predicate failed on the element 60, the method didn’t check the further elements.

Java 9 – Stream takeWhile() method
The method takeWhile() works just opposite to the dropWhile() method. This method takes all the elements of the stream in the resulted stream until the predicate fails. In short, when the predicate fails, it drops that element and all the elements that comes after that element in the stream. Lets take few examples to understand this.
Using takeWhile() method on an ordered Stream
Here the stream is ordered and the takeWhile() method takes all the elements until the predicate fails at element value 60.
jshell> Stream<Integer> mystream = Stream.of(10, 20, 30, 40, 60, 90, 120) mystream ==> java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head@2038ae61 jshell> mystream.takeWhile(num -> num < 50).forEach(num -> System.out.println(num)) 10 20 30 40
Using takeWhile() method on an unordered Stream
Similar to dropWhile() method, this method also doesn’t check the elements further once the predicate fails. This is why the elements 10 and 15 are dropped because they came after the element 60 (at which the predicate failed).
jshell> Stream<Integer> mystream = Stream.of(10, 20, 40, 60, 70, 10, 15, 100) mystream ==> java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head@21213b92 jshell> mystream.takeWhile(num -> num < 50).forEach(num -> System.out.println(num)) 10 20 40
Java 9 – Stream iterate() method
The iterate method in Java 9 has three arguments.
First argument is the initialising value, the returned stream starts with this value.
Second argument is the predicate, the iteration continues until this given predicate returns false.
Third argument updates the value of previous iteration.
Example:
In this example, the first argument is 1. The stream starts with the element 1.
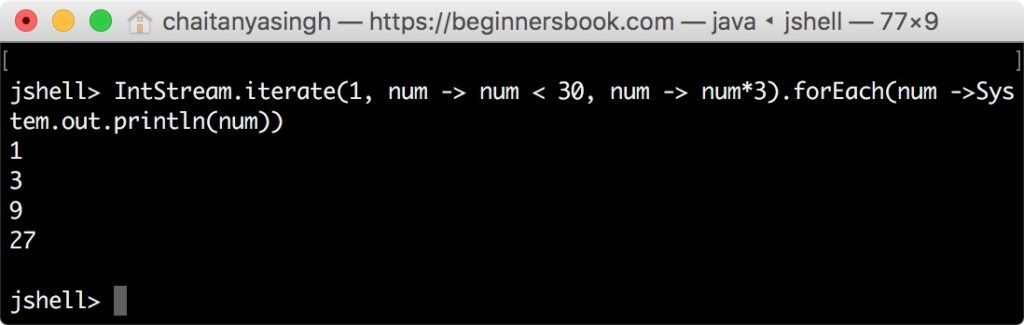
num -> num < 30 is the second argument and it is a predicate. The iteration continues until this returns false. num -> num*3 is the third argument that updates the value returned from previous iteration. This works similar to the counter variable of a loop.
jshell> IntStream.iterate(1, num -> num < 30, num -> num*3).forEach(num ->System.out.println(num)) 1 3 9 27
Starting the value 1, we are multiplying the returned value by 3 and this continues until the returned value is greater than 30.
Java 9 – Stream ofNullable() method
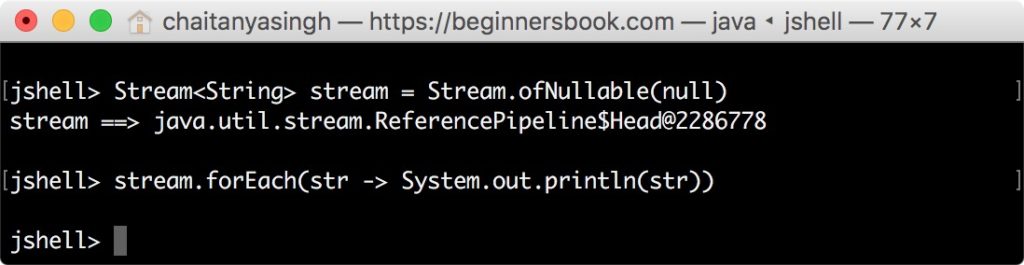
This method is introduced to avoid NullPointerException. This method returns an empty stream if the stream is null. It can also be used on a non-empty stream where it returns a sequential stream of single element.
Null Stream Example
jshell> Stream<String> stream = Stream.ofNullable(null) stream ==> java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head@2286778 jshell> stream.forEach(str -> System.out.println(str)) jshell>
Non-null Stream Example
jshell> Stream<String> stream = Stream.ofNullable("Rose")
stream ==> java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head@370736d9
jshell> stream.forEach(str -> System.out.println(str))
Rose
jshell>
These are the four Stream API enhancements that are done in Java SE 9.
Leave a Reply