Java Math.max() returns the greater number between two passed numbers. In this tutorial, we will discuss this method in detail with the help of examples.
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
float num = -15.5f;
float num2 = -5.55f;
//This will print the greater float number
System.out.println(Math.max(num, num2));
double d1 = 1001.22;
double d2 = 2500.33;
//This will print the greater double number
System.out.println(Math.max(d1, d2));
}
}
Output:
-5.55 2500.33
Syntax of Math.max() Method:
System.out.println(Math.max(101, 102)); //print 102
max() Description:
public static int max(int a, int b): Compares the passed int numbers and returns the greater integer number. This method has total four variations in the Math class to compare different data types such as float, long and double. These variations are:
public static int max(int a, int b); public static long max(long a, long b); public static float max(float a, float b); public static double max(double a, double b);
max() Parameters
This method takes two parameters:
- a: The first argument.
- b: The second argument.
max() Return Values
- Returns the greater number between a and b.
- If one argument is positive and other is negative then max() returns positive argument.
- If the arguments are NaN (Not a Number) then NaN is returned.
- If both the arguments are negative then the argument with lower absolute value is returned. For example: -15 and -5, the max number is -5.
Example 1: Max of two int numbers
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int x = -10;
int y = -20;
System.out.println("Max of a and b: "+Math.max(a,b));
System.out.println("Max of x and y: "+Math.max(x,y));
}
}
Output:
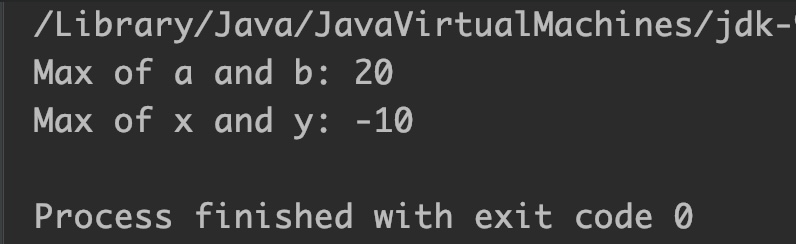
Example 2: Max of two float numbers
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
float a = 5.5f, b = 20.56f;
float x = -5.5f, y = -20.56f;
System.out.println("Max of a and b: "+Math.max(a,b));
System.out.println("Max of x and y: "+Math.max(x,y));
}
}
Output:
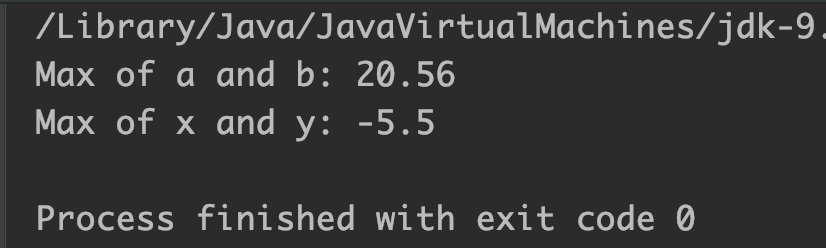
Example 3: Max of two double numbers
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
double a = 5000, b = 8000;
double x = -5000, y = -8000;
System.out.println("Max of a and b: "+Math.max(a,b));
System.out.println("Max of x and y: "+Math.max(x,y));
}
}
Output:
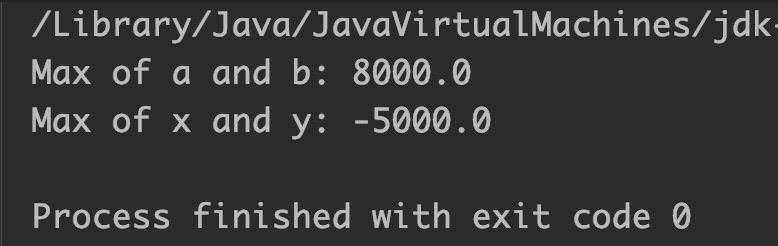
Example 4: Math.Max() Method with NaN
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
double x =0.0/0; //NaN (Not a Number)
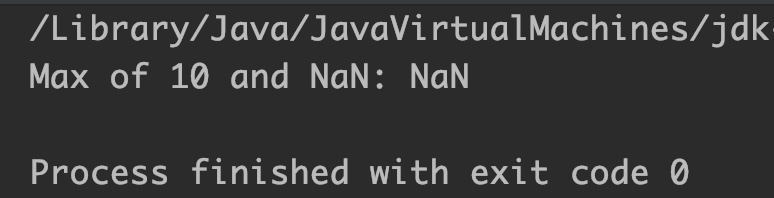
System.out.println("Max of 10 and NaN: "+Math.max(10, x));
}
}
Output: