Java Math.exp() method returns e raised to the power of given argument. Here e is a Euler’s number, whose approximate value is 2.718281828459045.
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double num = 1;
// returns e (approx. 2.718281828459045) to power of 1
System.out.println(Math.exp(num));
}
}
Output:
2.718281828459045
Syntax of Math.exp() method
Math.exp(2); //returns 7.38905609893065
exp() Description
public static double exp(double num): Returns e raised to the power a double argument num.
exp() Parameters
- num: Exponent double value. Passed as an argument to the method.
exp() Return Value
- Returns enum.
- If the argument is NaN (Not a number), then it returns NaN.
- If the argument is positive infinity, then it returns positive infinity.
- If the argument is negative infinity, then it returns positive zero.
Example 1
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double num = 10, num2 = 2;
System.out.println(Math.exp(num));
System.out.println(Math.exp(num2));
}
}
Output:

Example 2
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
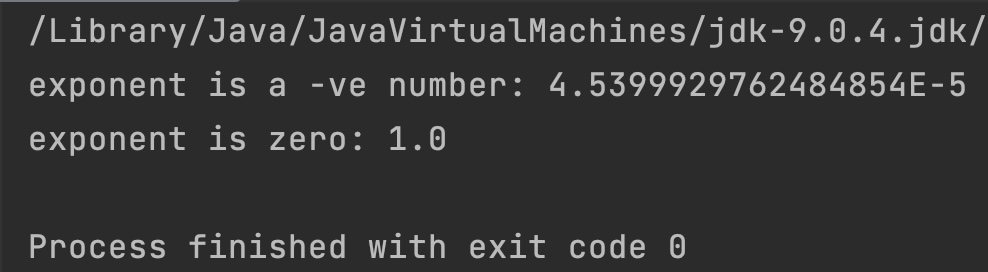
double num = -10, num2 = 0;
System.out.println("exponent is a -ve number: "+Math.exp(num));
System.out.println("exponent is zero: "+Math.exp(num2));
}
}
Output:
Example 3
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double num = 0.0/0, num2 = 4.0/0;
System.out.println("exponent is NaN: "+Math.exp(num));
System.out.println("exponent is +ve Infinity: "+Math.exp(num2));
}
}
Output:
