HashMap is a Map based collection class that is used for storing Key & value pairs, it is denoted as HashMap<Key, Value> or HashMap<K, V>. HashMap in java, is similar to the Hashtable class except that it is unsynchronized and permits nulls(null values and null key).
It is not an ordered collection which means it does not return the keys and values in the same order in which they have been inserted into the HashMap. It does not sort the stored keys and values. You must need to import java.util.HashMap or its super class in order to use the HashMap class and methods.
HashMap
Let’s discuss HashMap in detail.
- In key-value pairs, the key must be unique.
- It is non-synchronized. However you can make it synchronized.
- Doesn’t maintain insertion order.
- Doesn’t sort elements
- It allows null keys and values. However only one null key is allowed. Multiple null values are allowed.
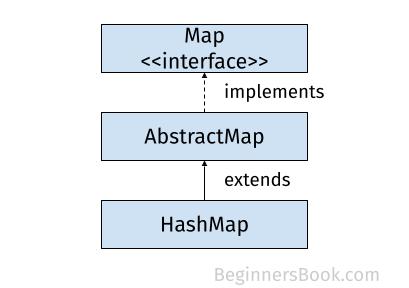
HashMap class hierarchy
How to declare HashMap in Java?
HashMap<K, V> hmap = new HashMap<K, V>();
K: It represents the type of the key in a key-value pair.
V: It represents the type of a value in a key-value pair.
For example: A HashMap that has integer keys and string values can be declared like this:
HashMap<Integer, String> hmap = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
HashMap in Java Examples
1. Adding elements to HashMap
You can use the put() method of the HashMap class to add new key-value pairs to the HashMap. To iterate the HashMap, we are using entrySet() method. This method returns an equivalent Set. This is to pass the key-value pairs to the Map.Entry, which contains the methods getKey() and getValue() that we can use to print key-value pairs of HashMap. HashMap elements are traversed using for loop and key-value pairs are printed.
import java.util.*;
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
HashMap<Integer,String> hMap=new HashMap<>();
hMap.put(101,"Cricket");
hMap.put(105,"Hockey");
hMap.put(111,"Basketball");
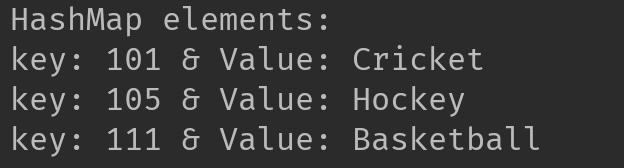
System.out.println("HashMap elements: ");
for(Map.Entry mEntry : hMap.entrySet()){
System.out.print("key: "+ mEntry.getKey() + " & Value: ");
System.out.println(mEntry.getValue());
}
}
}
Output:
2. Checking duplicate key insertion in HashMap
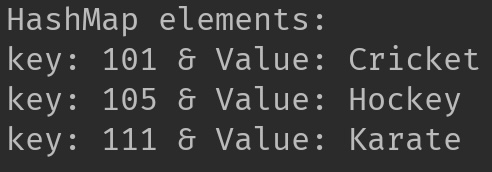
Here, we are trying to add element with a duplicate key. The new element (111,”Karate”) has the key value 111, which is already present in the HashMap. Instead of adding this new element, HashMap updated the value of already existing element with key “111”.
import java.util.*;
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
HashMap<Integer,String> hMap=new HashMap<>();
hMap.put(101,"Cricket");
hMap.put(105,"Hockey");
hMap.put(111,"Basketball");
hMap.put(111,"Karate"); //adding element with duplicate key
System.out.println("HashMap elements: ");
for(Map.Entry mEntry : hMap.entrySet()){
System.out.print("key: "+ mEntry.getKey() + " & Value: ");
System.out.println(mEntry.getValue());
}
}
}
Output:
3. HashMap remove() method Example
import java.util.*;
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
HashMap<Integer,String> hMap=new HashMap<>();
hMap.put(101,"Cricket");
hMap.put(105,"Hockey");
hMap.put(111,"Basketball");
//this will remove the key-value pair where
//the value of the key is 101
hMap.remove(101);
System.out.println("HashMap elements: ");
for(Map.Entry mEntry : hMap.entrySet()){
System.out.print("key: "+ mEntry.getKey() + " & Value: ");
System.out.println(mEntry.getValue());
}
}
}
Output:
HashMap elements: key: 105 & Value: Hockey key: 111 & Value: Basketball
4. HashMap replace() method Example
import java.util.*;
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
HashMap<Integer,String> hMap=new HashMap<>();
hMap.put(101,"Cricket");
hMap.put(105,"Hockey");
hMap.put(111,"Basketball");
//this will update the value of key-value pair
//where the key is 105
hMap.replace(105, "Kickboxing");
System.out.println("HashMap elements: ");
for(Map.Entry mEntry : hMap.entrySet()){
System.out.print("key: "+ mEntry.getKey() + " & Value: ");
System.out.println(mEntry.getValue());
}
}
}
Output:
HashMap elements: key: 101 & Value: Cricket key: 105 & Value: Kickboxing key: 111 & Value: Basketball
Internal working of HashMap in Java
HashMap internally uses a technique called hashing to generate index for keys. This indexing allows faster searching of record. This allows faster response time for operations such as search, update, delete etc.
When we call the HashMap put() method as shown in the following statement. It calculates the hash code of the key (101 in this case) using hash function. This hash code is calculated using the hashing technique. An index is assigned to this hash code. This index uniquely identifies this key-value pair.
HashMap<Integer,String> hMap=new HashMap<>(); hMap.put(101,"Cricket");
When a duplicate key is inserted into the HashMap, Hash Collision happens. HashMap handles this by updating the old value with the new value.
HashMap Class Methods
Here is the list of methods available in HashMap class. I have also covered examples using these methods at the end of this post.
- void clear(): It removes all the key and value pairs from the specified Map.
- Object clone(): It returns a copy of all the mappings of a map and used for cloning them into another map.
- boolean containsKey(Object key): It is a boolean function which returns true or false based on whether the specified key is found in the map.
- boolean containsValue(Object Value): Similar to containsKey() method, however it looks for the specified value instead of key.
- Value get(Object key): It returns the value for the specified key.
- boolean isEmpty(): It checks whether the map is empty. If there are no key-value mapping present in the map then this function returns true else false.
- Set keySet(): It returns the Set of the keys fetched from the map.
- value put(Key k, Value v): Inserts key value mapping into the map. Used in the above example.
- int size(): Returns the size of the map – Number of key-value mappings.
- Collection values(): It returns a collection of values of map.
- Value remove(Object key): It removes the key-value pair for the specified key. Used in the above example.
- void putAll(Map m): Copies all the elements of a map to the another specified map.
HashMap Example to demonstrate various methods
In this example we have demonstrated almost all the important methods of HashMap class.
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class Details {
public static void main(String args[]) {
/* This is how to declare HashMap */
HashMap<Integer, String> hmap = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
/*Adding elements to HashMap*/
hmap.put(12, "Chaitanya");
hmap.put(2, "Rahul");
hmap.put(7, "Singh");
hmap.put(49, "Ajeet");
hmap.put(3, "Anuj");
/* Display content using Iterator*/
Set set = hmap.entrySet();
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry mentry = (Map.Entry)iterator.next();
System.out.print("key is: "+ mentry.getKey() + " & Value is: ");
System.out.println(mentry.getValue());
}
/* Get values based on key*/
String var= hmap.get(2);
System.out.println("Value at index 2 is: "+var);
/* Remove values based on key*/
hmap.remove(3);
System.out.println("Map key and values after removal:");
Set set2 = hmap.entrySet();
Iterator iterator2 = set2.iterator();
while(iterator2.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry mentry2 = (Map.Entry)iterator2.next();
System.out.print("Key is: "+mentry2.getKey() + " & Value is: ");
System.out.println(mentry2.getValue());
}
}
}
Output:
key is: 49 & Value is: Ajeet key is: 2 & Value is: Rahul key is: 3 & Value is: Anuj key is: 7 & Value is: Singh key is: 12 & Value is: Chaitanya Value at index 2 is: Rahul Map key and values after removal: Key is: 49 & Value is: Ajeet Key is: 2 & Value is: Rahul Key is: 7 & Value is: Singh Key is: 12 & Value is: Chaitanya
HashMap Tutorials
Here is the list of tutorials published on HashMap class. Happy Learning:)
HashMap Basics
- How to iterate HashMap
- Sort HashMap by Keys and values
- Get Size of HashMap
- Remove Key-value mapping from HashMap
- Remove all mapping from HashMap
- How to check if HashMap is empty or not?
Raju says
Mind Blowing……
Do something so that your website can have more views………this is very much useful for beginners……………….
Chaitanya Singh says
Thanks for your kind words Raju :)
piyush shukla says
very good explanation…
May says
Hi Chaitanya,
This tutorial is really very understandable.
I have been trying to learn Java from a long time but am not really able to get to undertsand the concepts well enough to use them wherever needed. Can you please suggest me how to learn so I can use the concepts in my day today job.
Farhan Ali says
Hello Sir,
I don’t understand why have you used set for iterating while it can be easily done with keySet();.
sunny says
keyset() also return SET.
but if you use KeySet() – it will just return all keys in one go but if you want to traverse each key and do some operation you required something else and the same was explained by Chaitanya..
Hope this help!
Line says
Why do I get NullPointerException?
Tamil selvan s says
There may be no objects available at that area or space in which you are accessing.
For example we can take an array
int a[] = new int[5];
here the available values are a[0],a[1],a[2],a[3],a[4] if u try to fix values for a[5] then you will get nullpointerexception!!!!!!!
Andrew says
I want to know why the order of the output is not the same as we input them. Would you mind email me your reply? Thanks!
Max Bradley says
Hi Andrew,
I was wondering the same, I think it is just a property of HashMaps that there is no ordering. When you add items to them you are not adding after any existing entries, you are just added to a pool of key-value pairs.
Karthi says
Read these lines again please
It is not an ordered collection which means it does not return the keys and values in the same order in which they have been inserted into the Hash Map. It does not sort the stored keys and Values.