In the last tutorial we discussed for loop. In this tutorial we will discuss while loop. As discussed earlier, loops are used for executing a block of program statements repeatedly until the given loop condition returns false.
Syntax of while loop
while(condition)
{
statement(s);
}
How while Loop works?
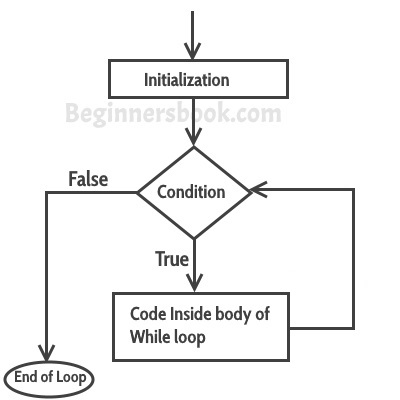
In while loop, condition is evaluated first and if it returns true then the statements inside while loop execute, this happens repeatedly until the condition returns false. When condition returns false, the control comes out of loop and jumps to the next statement in the program after while loop.
Note: The important point to note when using while loop is that we need to use increment or decrement statement inside while loop so that the loop variable gets changed on each iteration, and at some point condition returns false. This way we can end the execution of while loop otherwise the loop would execute indefinitely.
Flow Diagram of While loop
While Loop example in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int i=1;
/* The loop would continue to print
* the value of i until the given condition
* i<=6 returns false.
*/
while(i<=6){
cout<<"Value of variable i is: "<<i<<endl; i++;
}
}
Output:
Value of variable i is: 1 Value of variable i is: 2 Value of variable i is: 3 Value of variable i is: 4 Value of variable i is: 5 Value of variable i is: 6
Infinite While loop
A while loop that never stops is said to be the infinite while loop, when we give the condition in such a way so that it never returns false, then the loops becomes infinite and repeats itself indefinitely.
An example of infinite while loop:
This loop would never end as I’m decrementing the value of i which is 1 so the condition i<=6 would never return false.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int i=1; while(i<=6) {
cout<<"Value of variable i is: "<<i<<endl; i--;
}
}
Example: Displaying the elements of array using while loop
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int arr[]={21,87,15,99, -12};
/* The array index starts with 0, the
* first element of array has 0 index
* and represented as arr[0]
*/
int i=0;
while(i<5){
cout<<arr[i]<<endl;
i++;
}
}
Output:
21 87 15 99 -12
Leave a Reply