Set is an unordered and unindexed collection of items in Python. Unordered means when we display the elements of a set, it will come out in a random order. Unindexed means, we cannot access the elements of a set using the indexes like we can do in list and tuples.
The elements of a set are defined inside curly brackets and are separated by commas. For example –
myset = {1, 2, 3, 4, "hello"}
Python Set Example
# Set Example
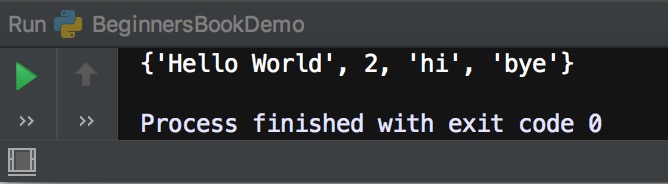
myset = {"hi", 2, "bye", "Hello World"}
print(myset)
Output:
Checking whether an item is in the set
We can check whether an item exists in Set or not using “in” operator as shown in the following example. This returns the boolean value true or false. If the item is in the given set then it returns true, else it returns false.
# Set Example
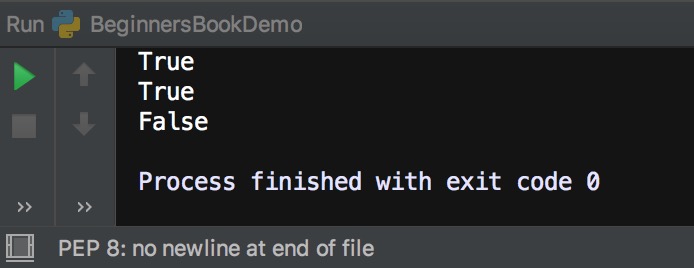
myset = {"hi", 2, "bye", "Hello World"}
# checking whether 2 is in myset
print(2 in myset)
# checking whether "hi" is in myset
print("hi" in myset)
# checking whether "BeginnersBook" is in myset
print("BeginnersBook" in myset)
Output:
Loop through the elements of a Set in Python
We can loop through the elements of a set in Python as shown in the following elements. As you can see in the output that the elements will appear in random order each time you run the code.
# Set Example
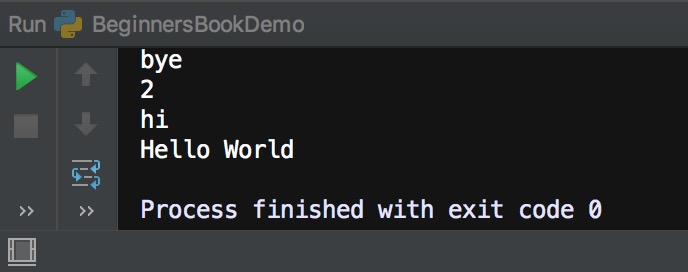
myset = {"hi", 2, "bye", "Hello World"}
# loop through the elements of myset
for a in myset:
print(a)
Output:
Python – Add or remove item from a Set
We can add an item in a Set using add() function and we can remove an item from a set using remove() function as shown in the following example.
# Set Example
myset = {"hi", 2, "bye", "Hello World"}
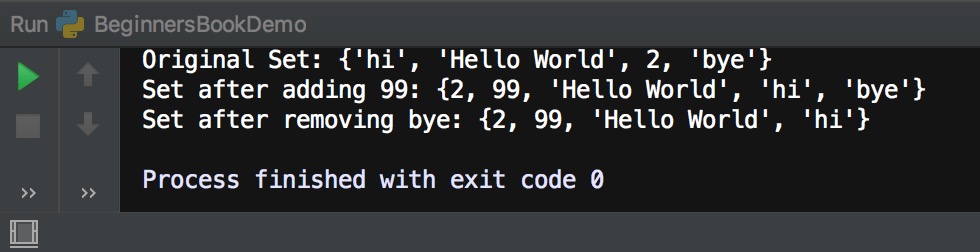
print("Original Set:", myset)
# adding an item
myset.add(99)
print("Set after adding 99:", myset)
# removing an item
myset.remove("bye")
print("Set after removing bye:", myset)
Output:
Set Methods
1. add(): This method adds an element to the Set.
2. remove(): This method removes a specified element from the Set
3. discard(): This method works same as remove() method, however it doesn’t raise an error when the specified element doesn’t exist.
4. clear(): Removes all the elements from the set.
5. copy(): Returns a shallow copy of the set.
6. difference(): This method returns a new set which is a difference between two given sets.
7. difference_update(): Updates the calling set with the Set difference of two given sets.
8. intersection(): Returns a new set which contains the elements that are common to all the sets.
9. intersection_update(): Updates the calling set with the Set intersection of two given sets.
10. isdisjoint(): Checks whether two sets are disjoint or not. Two sets are disjoint if they have no common elements.
11. issubset(): Checks whether a set is a subset of another given set.
12. pop(): Removes and returns a random element from the set.
13. union(): Returns a new set with the distinct elements of all the sets.
14. update(): Adds elements to a set from other passed iterable.
15. symmetric_difference(): Returns a new set which is a symmetric difference of two given sets.
16. symmetric_difference_update(): Updates the calling set with the symmetric difference of two given sets.
Leave a Reply