In this guide, you will learn how to implement merge sort algorithm in Java.
What is a Merge Sort in Java?
Merge sort algorithm is used to sort a group of elements. It is a general purpose comparison based algorithm. Merge sort is based on the principe of divide-and-conquer approach that was invented by John von Neumann in 1945.
How it works? Merge sort algorithm works by dividing a bigger problem into smaller problems. These smaller problems are further divided into sub-problems. These sub problems are solved individually and the outcome of these smaller problems is combined to get the solution of main problem.
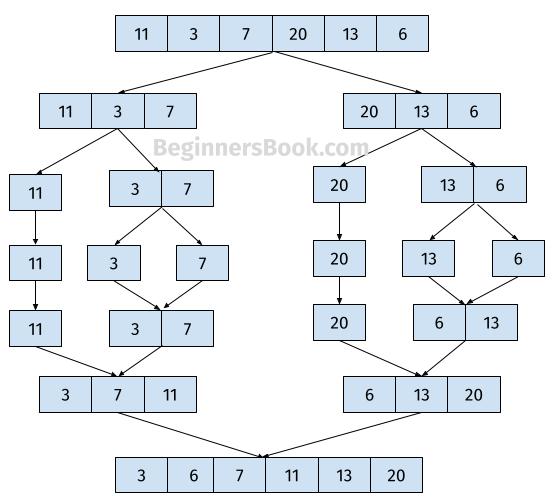
Program to implement Merge Sort in java
// Implement Merge sort algorithm in Java
import java.util.Arrays;
class JavaExample {
// Merge two sub arrays L and R into array
void merge(int array[], int lSide, int mid, int rSide) {
//setting size of left and right array
int len1 = mid - lSide + 1;
int len2 = rSide - mid;
int L[] = new int[len1];
int R[] = new int[len2];
// filling the L and R arrays
for (int i = 0; i < len1; i++)
L[i] = array[lSide + i];
for (int j = 0; j < len2; j++)
R[j] = array[mid + 1 + j];
// Maintain current index of sub-arrays and main array
int i, j, k;
i = 0;
j = 0;
k = lSide;
// Until we reach the end of either left or right array, compare
// corresponding elements of L and R array and place the
// smaller element in the array to maintain the ascending order.
// for sorting in descending order use if(L[i] >= <[j])
while (i < len1 && j < len2) {
if (L[i] <= R[j]) {
array[k] = L[i];
i++;
} else {
array[k] = R[j];
j++;
}
k++;
}
// Place the remaining elements in the array
while (i < len1) {
array[k] = L[i];
i++;
k++;
}
while (j < len2) {
array[k] = R[j];
j++;
k++;
}
}
// Divide the array into two sub arrays, sort them using recursion and
// merge them by calling the method merge() that we have created above
void mergeSort(int array[], int firstIndex, int lastIndex) {
if (firstIndex < lastIndex) {
// m is mid point that is the division point
int mid = (firstIndex + lastIndex) / 2;
// recursive call to this method by passing the sub arrays
mergeSort(array, firstIndex, mid);
mergeSort(array, mid + 1, lastIndex);
// Merge the sorted sub arrays by calling merge() method
merge(array, firstIndex, mid, lastIndex);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
// unsorted array
int[] array = { 11, 3, 7, 20, 13, 6 };
System.out.println("Unsorted Array: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
JavaExample obj = new JavaExample();
// calling the method mergeSort() to sort the array
// firstIndex is 0 (first element), lastIndex is size-1
obj.mergeSort(array, 0, array.length - 1);
System.out.println("Sorted Array: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
}
Output:
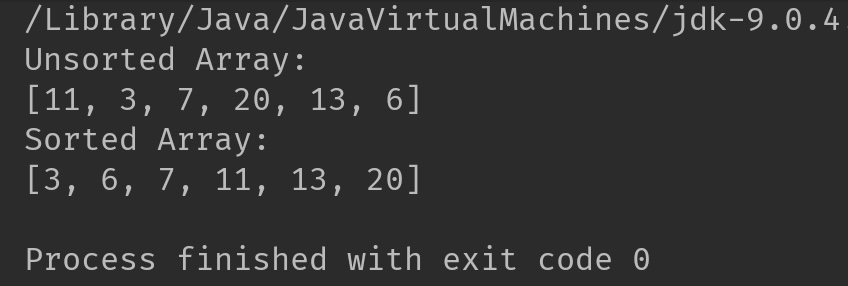
In the above program, we are calling the mergeSort() method. This method breaks the passed array into small subarrays using recursion. These subarrays are sorted individually and then merged together to form the solution for original array.
Related Java Programs
- Java Program for Selection Sort
- Java Program to perform Bubble sort on Strings
- Java Program to perform Binary Search
- Java Program to perform Linear Search