Exception handling is one of the most important feature of java programming that allows us to handle the runtime errors caused by exceptions. In this guide, you will learn what is an exception, types of it, exception classes and how to handle exceptions in java with examples.
What is an exception?
An Exception is an unwanted event that interrupts the normal flow of the program. When an exception occurs program execution gets terminated. In such cases we get a system generated error message.
The good thing about exceptions is that java developer can handle these exception in such a way so that the program doesn’t get terminated abruptly and the user get a meaningful error message.
For example: You are writing a program for division and both the numbers are entered by user. In the following example, user can enter any number, if user enters the second number (divisor) as 0 then the program will terminate and throw an exception because dividing a number by zero gives undefined result. To get the user input, we are using Scanner class. Notice the output of the program.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1, num2;
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter first number(dividend): ");
num1 = scan.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter second number(divisor): ");
num2 = scan.nextInt();
int div = num1/num2;
System.out.println("Quotient: "+div);
}
}
Output:
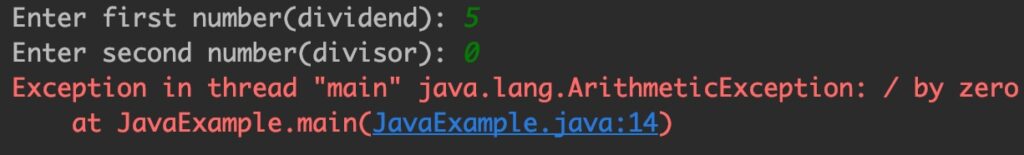
As you can see, the user input caused the program to throw Arithmetic exception, however this is not a good programming practice to leave such exceptions unhandled. Let’s handle this exception.
Exception Handling in Java
Here, we are trying to handle the exception that is raised in the above program. You can see that the program ran fine and gave a meaningful error message which can be understood by the user.
Note: Do not worry about the try and catch blocks as we have covered these topics in detail in separate tutorials. For now just remember that the code that can throw exception needs to be inside try block and the catch block follows the try block, where the exception error message is set.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1, num2;
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter first number(dividend): ");
num1 = scan.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter second number(divisor): ");
num2 = scan.nextInt();
try {
int div = num1 / num2;
System.out.println("Quotient: "+div);
}catch(ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("Do not enter divisor as zero.");
System.out.println("Error Message: "+e);
}
}
}
Output:
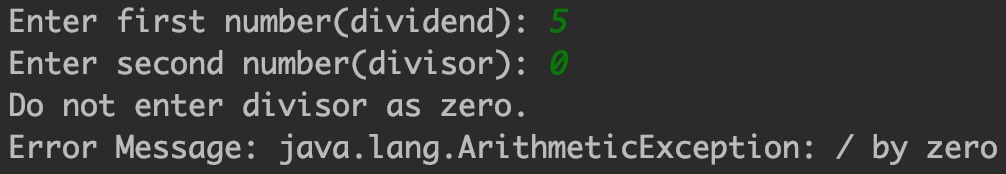
If an exception occurs, which has not been handled by programmer then program execution gets terminated and a system generated error message is shown to the user.
These system generated messages are not user friendly so a user will not be able to understand what went wrong. In order to let them know the reason in simple language, we handle exceptions. We handle such exceptions and then prints a user friendly warning message to user, which lets them correct the error as most of the time exception occurs due to bad data provided by user.
Why we handle the exceptions?
Exception handling ensures that the flow of the program doesn’t break when an exception occurs. For example, if a program has bunch of statements and an exception occurs mid way after executing certain statements then the statements, that occur after the statement that caused the exception will not execute and the program will terminate abruptly. By handling we make sure that all the statements execute and the flow of execution of program doesn’t break.
Why an exception occurs?
There can be several reasons that can cause a program to throw exception. For example: Opening a non-existing file in your program, Network connection problem, bad input data provided by user etc. Let’s see few scenarios:
1. ArithmeticException:
We have already seen this exception in our example above. This exception occurs when we divide a number by zero. If we divide any number by zero.
int num = 25/0;//ArithmeticException
2. NullPointerException:
When a variable contains null value and you are performing an operation on the variable. For example, if a string variable contains null and you are comparing with another string. Another example is when you are trying to print the length of the string that contains null.
String str = null; //NullPointerException System.out.println(str.length());
3. NumberFormatException:
This exception occurs where there is a type mismatch. Let’s say you are trying to perform an arithmetic operator on a string variable.
String str = "beginnersbook.com"; //NumberFormatException int num=Integer.parseInt(str);
4. ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:
When you are trying to access the array index which is beyond the size of array. Here, we are trying to access the index 8 (9th element) but the size of the array is only 3. This exception occurs when you are accessing index which doesn’t exist.
int arr[]=new int[3]; //ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException arr[8]=100;
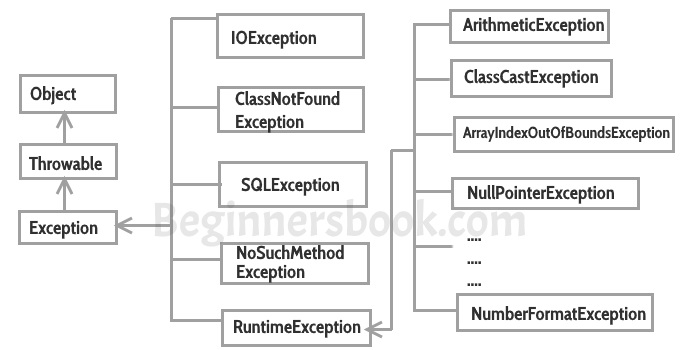
Difference between error and exception
Errors indicate that something went wrong which is not in the scope of a programmer to handle. You cannot handle an error. Also, the error doesn’t occur due to bad data entered by user rather it indicates a system failure, disk crash or resource unavailability.
Exceptions are events that occurs during runtime due to bad data entered by user or an error in programming logic. A programmer can handle such conditions and take necessary corrective actions. Few examples:
NullPointerException – When you try to use a reference that points to null.
ArithmeticException – When bad data is provided by user, for example, when you try to divide a number by zero this exception occurs because dividing a number by zero is undefined.
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException – When you try to access the elements of an array out of its bounds, for example array size is 5 (which means it has five elements) and you are trying to access the 10th element.
Types of exceptions
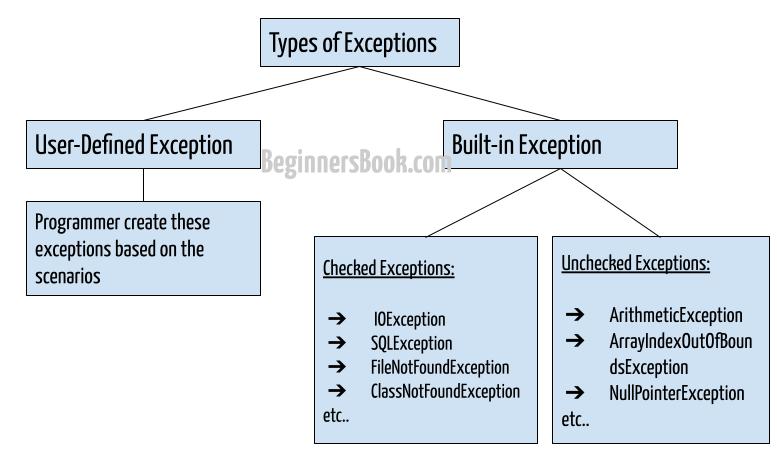
There are two types of exceptions in Java:
1) Checked exceptions
2) Unchecked exceptions
I have covered these topics in detail in a separate tutorial: Checked and Unchecked exceptions in Java.
1) Checked exceptions
All exceptions other than Runtime Exceptions are known as Checked exceptions as the compiler checks them during compilation to see whether the programmer has handled them or not. If these exceptions are not handled/declared in the program, you will get compilation error. For example, SQLException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException etc.
2) Unchecked Exceptions
Runtime Exceptions are also known as Unchecked Exceptions. These exceptions are not checked at compile-time so compiler does not check whether the programmer has handled them or not but it’s the responsibility of the programmer to handle these exceptions and provide a safe exit.
For example, ArithmeticException, NullPointerException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException etc. The examples that we seen above were unchecked exceptions.
Note: Compiler doesn’t enforce you to catch such exceptions or ask you to declare it in the method using throws keyword.
Frequently used terms in Exception handling
try: The code that can cause the exception, is placed inside try block. The try block detects whether the exception occurs or not, if exception occurs, it transfer the flow of program to the corresponding catch block or finally block. A try block is always followed by either a catch block or finally block.
catch: The catch block is where we write the logic to handle the exception, if it occurs. A catch block only executes if an exception is caught by the try block. A catch block is always accompanied by a try block.
finally: This block always executes whether an exception is occurred or not.
throw: It is used to explicitly throw an exception. It can be used to throw a checked or unchecked exception.
throws: It is used in method signature. It indicates that this method might throw one of the declared exceptions. While calling such methods, we need to handle the exceptions using try-catch block.
What topics are covered in the next tutorials
You can read these topics to understand the exception handling concept in detail. You can also practice various programs covered in the following tutorials.
sravani says
hi Chaitanya Singh,
thanks for your efforts it is really appreciated.this is the best site i have ever seen. very clear explanation. please upload the frameworks also.then it will be very helpful to us.
Poornima says
Explanation is good… Thanks
akash says
good reply
satyabrata barik says
Hi Chaitanya,
Thanks a lot for putting such hard work for us and I can say this is the most simplest website where the beginners really will be start focusing. It helped me and I usually go through your others subject when i get some time.
sampath says
Am Lecturer in Computer Science, This site is an Excellent site. Very Good Explanation and easy understandable examples. very good. update frequently.
kumar vishal says
Explanation is good.But, try to give more examples. Examples are so easy. For programming examples should be more for practices.
Harsh says
Please tell me how to handle checked and unchecked exception with example?
Ashfaq says
Same mechanism is used to handle any exception. Difference between checked and unchecked exception is that if you don’t handle checked exception using try…catch block in your program then it will not compile.
Vikram says
Hi,
THis is very good site having explanation of core concepts in very simple manner.
Regards
Vikram
chandrasekhar says
Hi Chaitanya,
beginnersbook helped me a lot.Thank you.
Abhinav Kumar says
Hi Chaitanya,
Beginners Book is really one of the best to the ground sites for the basic JAVA learners.
Thanks a lot for it…!!
hajra says
thank you so much for a simple and clear explanation…
Nawal Sah says
What is the difference between compiler error and exception?
praveen says
Compiler error:when we compile the program then we will get compile time error.
Exception:an unwanted unexpected event disturbs the normal flow of the program execution.
Nawal Sah says
What code block should we never return from and why?
Nawal Sah says
What is Error? Can we catch Errors? If yes, what should be done in the catch block and why?
Chitra says
thanks a lot.. it is nice blog to know the java concepts.. simple and easy yar… :)
Brian Wekesa says
good work I enjoyed reading it……….#bryan
Sandor Szekeres says
“When an exception occurs program processing gets terminated and doesn’t continue further.”
It is not strictly true… If we handle the exception correctly then it can continue processing.
Am I right?
See the first exception of this article:
https://beginnersbook.com/2013/04/try-catch-in-java/
Deepan says
The way you have explained is really awesome, also you have provided the examples where ever required.
thanks for your great effort.
Gajanan Kharat says
Hello Chaitanya,
Nice explanation about Exception handling but Could you please elaborate How ClassNotFoundException
comes under the “Checked Exception”, I guess it should be unchecked exception