Java Math.asin() method returns arc sine of the given value. Arc sine is the inverse of the sine function. The value returned by this method ranges between -pi/2 and pi/2.
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double a = 1.0;
System.out.println(Math.asin(a));
}
}
Output:
1.5707963267948966
Syntax of Math.asin() method
Math.asin(0); //returns 0.0
asin() Description
public static double asin(double a): Returns the arc sine of the given double value a.
asin() Parameters
- a: A double type value whose arc sine is to be determined.
asin() Return Value
- The arc sine of the argument.
- If the argument is NaN (Not a number) or its absolute value is greater than 1, then it returns NaN.
- If the argument is zero, then it returns zero with the same sign.
Example 1
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double d1 = 1.0;
double d2 = 0;
double d3 = -1.0;
System.out.println(Math.asin(d1));
System.out.println(Math.asin(d2));
System.out.println(Math.asin(d3));
}
}
Output:

Example 2
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double d1 = Double.MAX_VALUE;
double d2 = Double.MIN_VALUE;
double d3 = 0.0/0; //NaN
System.out.println(Math.asin(d1));
System.out.println(Math.asin(d2));
System.out.println(Math.asin(d3));
}
}
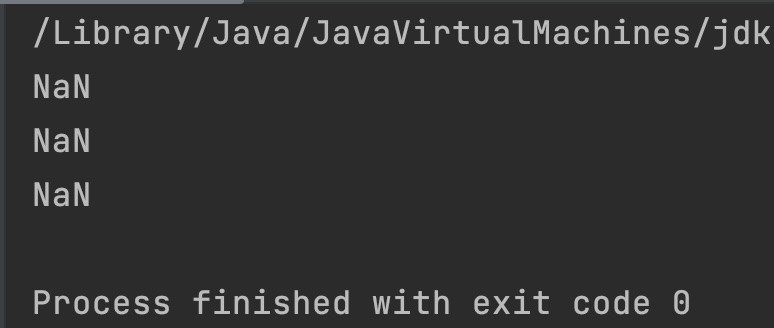
Output:

Example 3
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double d1 = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
double d2 = Double.NEGATIVE_INFINITY;
double d3 = Math.PI;
System.out.println(Math.asin(d1));
System.out.println(Math.asin(d2));
System.out.println(Math.asin(d3));
}
}
Output: