Java Math.acos() method returns arc cosine of the given value. Arc cosine is the inverse of cosine function. The value returned by this method ranges between 0.0 and pi.
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double a = 1.0;
System.out.println(Math.acos(a));
}
}
Output:
0.0
Syntax of Math.acos() method
Math.acos(-1); //returns 3.141592653589793
acos() Description
public static double acos(double a): Returns arc cosine of the double prevision value a.
acos() Parameters
- a: A double precision value whose arc cosine is to be determined.
acos() Return Value
- Arc cosine of the argument.
- If the argument is NaN (Not a number) or its absolute value is greater than 1, then it returns NaN.
Example 1
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
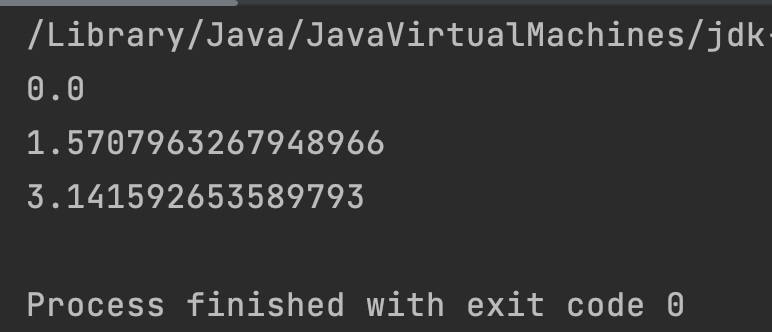
double d1 = 1.0;
double d2 = 0;
double d3 = -1.0;
System.out.println(Math.acos(d1));
System.out.println(Math.acos(d2));
System.out.println(Math.acos(d3));
}
}
Output:
Example 2
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
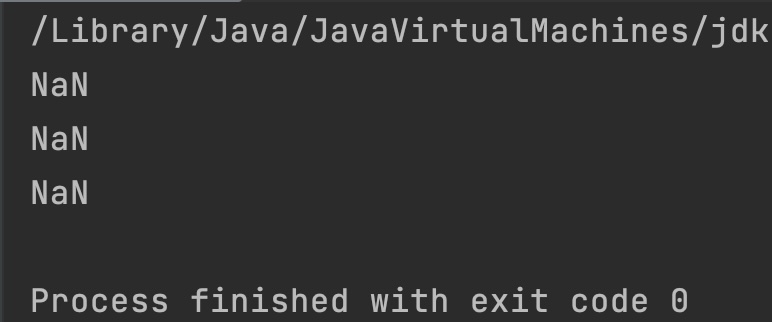
double d1 = Double.MAX_VALUE;
double d2 = Double.MIN_VALUE;
double d3 = 0.0/0; //NaN
System.out.println(Math.acos(d1));
System.out.println(Math.acos(d2));
System.out.println(Math.acos(d3));
}
}
Output:
Example 3
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
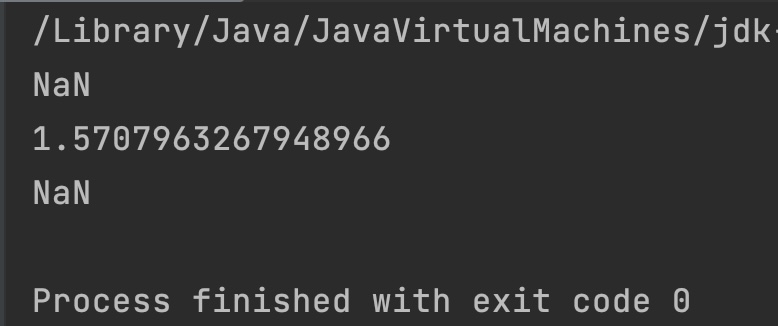
double d1 = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
double d2 = Double.NEGATIVE_INFINITY;
double d3 = Math.PI;
System.out.println(Math.acos(d1));
System.out.println(Math.acos(d2));
System.out.println(Math.acos(d3));
}
}
Output: