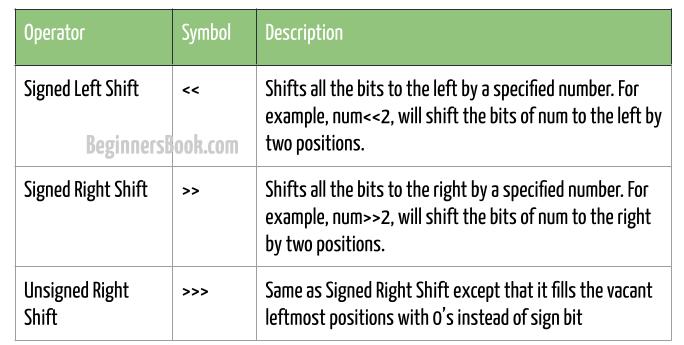
Shift operators are used to perform bit manipulation. In this guide, we will discuss various shift operators in java with the help of examples. Java supports following shift operators:
1. Signed Left Shift Operator (<<) Example
Left shift operator is denoted by << symbol. It shifts all bits towards left by a certain number of specified bits, for example: num<<2 will shift the bits of number num to the left by two positions. The bit positions that have been vacated by the left shift operator are filled with 0’s.
38 = 00100110 (In binary)
38<<2 = 10011000 (In binary) [Left shift by two bits]
= 152 (In decimal)
Program:
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x = 38, y = -38;
//left shift by two positions, for the negative number
//y, the sign is preserved in signed left shift
System.out.println("x<<2: " + (x<<2));
System.out.println("y<<2: " + (y<<2));
}
}
Output:
x<<2: 152 y<<2: -152
2. Signed Right Shift Operator (>>) Example
Right shift operator is denoted by >> symbol. It shifts all bits towards right by certain number of specified bits. For example: num>>2 will shift the bits to the right by two positions. The bit positions that have been vacated by the right shift operator are filled with 0’s.
32 = 00100000 (In binary)
32>>2 = 00001000 (In binary) [Right shift by two bits]
= 8 (In decimal)
Program:
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x = 32, y = -32;
//Right shift by two positions, for the negative number
//y, the sign is preserved in signed right shift
System.out.println("x>>2: " + (x>>2));
System.out.println("y>>2: " + (y>>2));
}
}
Output:
x>>2: 8 y>>2: -8
3. Unsigned Right Shift Operator (>>>) Example
In Unsigned right shift operator, the sign bit is not preserved, thus the result of right shift is different between signed and unsigned shifts.
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
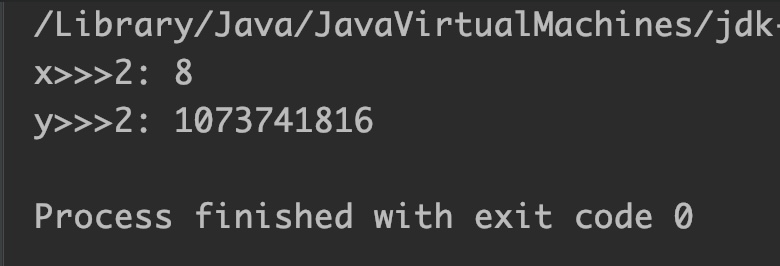
int x = 32, y = -32;
//Unsigned right shift
System.out.println("x>>>2: " + (x>>>2));
System.out.println("y>>>2: " + (y>>>2));
}
}
Output:
4. Unsigned Left Shift Operator (<<<) Example
There is no unsigned left shift operator <<< in java, this is because the result of << and <<< would produce same result.