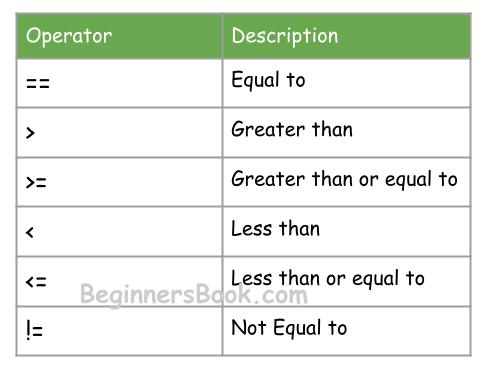
Relational operators are used to compare two operands. In this guide, we will discuss various relational operators in java with the help of examples. Java programming language supports following relational operators.
In any operation, there is an operator and operands. For example: In a+b, the “+” symbol is the operator and a & b are operands.
1. Equal to == Operator Example
The == operator checks whether two operands are equal or not. In the following example, we have two variables num1 and num2, we are using Equal to (==) operator to check whether these numbers are equal. In this example, we are comparing two numbers, we can compare two stings as well, using equals() method.
class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1 = 9, num2 = 9;
// == Operator is used to check whether num1 and num2 are equal or not
if(num1 == num2){
System.out.println("Numbers num1 and num2 are equal");
}
else{
System.out.println("Numbers num1 and num2 are not equal");
}
}
}
Output:
Numbers num1 and num2 are equal
Difference between = and == operator?
These operators looks similar however they are not same at all. The = operator is an assignment operator, it assigns a value to an operand on the left-hand side. The == operator is a relational operator which is used for comparison.
For example:
class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1, num2;
// = operator
num1 = 10; //This is assignment, value 10 is assigned to num1
num2 = 20; //Value 20 is assigned to num2
// == operator used here to compare the values of num1 & num2
// it returns either true or false. In this case, it returned false
// and that 'false' value is assigned to b using = operator
boolean b = (num1==num2);
System.out.println(b);
}
}
Output:
false
2. Greater than > Operator Example
var1 > var2 //var1 is left side operand, var2 is right side operand
The greater than > operator checks whether left-hand side operand is greater than right-hand side operand. If it is, then it returns true else it returns false.
class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1 = 10, num2 = 20, num3 = 5;
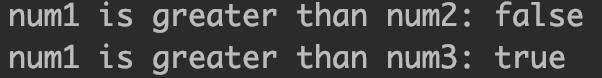
//checking whether num1 > num2
System.out.println("num1 is greater than num2: "+(num1>num2));
//checking whether num1 > num3
System.out.println("num1 is greater than num3: "+(num1>num3));
}
}
Output:
3. Greater than or equal to >= Operator Example
It checks whether left-hand side operand is greater than or equal to the right-hand side operand. If it is, then it returns true else it returns false.
Here we are demonstrating the difference between > and >=. In the following example, two numbers are equal, when we compared them using >, it returned false. However when we compared them using >= operator, it returned true, this is because >= returns true if left number is greater than or equal to the right number .
class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//declaring integer variables
int num1, num2;
//assigning values to variables using
//assignment operator
num1 = 100;
num2 = 100;
//Comparing using > operator
System.out.println("num1 > num2: "+(num1>num2));
//Comparing using >= operator
System.out.println("num1 >= num2: "+(num1>=num2));
}
}
Output:

4. Less than < Operator Example
The < Operator returns:
- If left side operand less than right side operand: true
- If left side operand greater than right side operand: false
- If left side operand is equal to right side operand: false
class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1 = 10, num2 = 20, num3 = 5;
//checking whether num1 is less than num2 using '<' operator
System.out.println("num1 is less than num2: "+(num1<num2));
//checking whether num1 is less than num3 using '<' operator
System.out.println("num1 is less than num3: "+(num1<num3));
}
}
Output:

5. Less than <= Operator Example
The only difference between < and <= operator is that <= operator returns true even if the operands are equal.
The <= Operator returns:
- If left side operand less than right side operand: true
- If left side operand greater than right side operand: false
- If left side operand is equal to right side operand: true
class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 100, y = 150, z = 100;
//checking whether x is less than or equal to y
System.out.println("x is less than or equal to y: "+(x<=y));
//checking whether x is less than or equal to z
System.out.println("x is less than or equal to z: "+(x<=z));
}
}
Output:

6. Not Equal to != Operator Example
The != operator checks whether the left-side operand is not equal to right-side operand, if the operands are not equal, it returns true else it returns false.
!= Operator returns: If left side operand equal to right side operand: false If left side operand not equal to right side operand: true
In this program, we have three integer variables, x and y are different, while x and z are same. The != returned “true” for x and y comparison because they are different. It returned “false” for x and z as they both are same.
class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 100, y = 150, z = 100;
//checking whether x is not equal to y
System.out.println("x is not equal to y: "+(x!=y));
//checking whether x is not equal to z
System.out.println("x is not equal to z: "+(x!=z));
}
}
Output:
x is not equal to y: true x is not equal to z: false