In this article, we will discuss the rint() method of Math class Java. We will see several programs with explanation to understand this method . Math.rint(double x) method returns the double value that is nearest to the given argument x and equal to a mathematical integer number.
This method rounds to the nearest integer, but if two integers are equally close, it rounds to the even integer. For example, for the number 2.5, this method would return 2, even though 2 and 3 are equally close because 2 is even.
Let’s see an example:
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double x = 32.5;
double x2 = 31.5;
//32 and 33 are equally close to x
//even number 32 is chosen
System.out.println(Math.rint(x));
//31 and 32 are equally close to x
//even number 32 is chosen
System.out.println(Math.rint(x2));
}
}
Output:
32.0 32.0
Another Example:
public class RintExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double[] values = { 2.3, 2.5, 2.7, -2.3, -2.5, -2.7, 3.5, 4.5 };
for (double value : values) {
double result = Math.rint(value);
System.out.println("Math.rint(" + value + ") = " + result);
}
}
}
Output:
Math.rint(2.3) = 2.0
Math.rint(2.5) = 2.0
Math.rint(2.7) = 3.0
Math.rint(-2.3) = -2.0
Math.rint(-2.5) = -2.0
Math.rint(-2.7) = -3.0
Math.rint(3.5) = 4.0
Math.rint(4.5) = 4.0
Explanation of the output
Math.rint(2.3)returns2.0as it is the closest integer to 2.3.Math.rint(2.5)returns2.0because, in this case 2 and 3 are equally close but even number is chosen. Here, 2 is even.Math.rint(2.7)returns3.0as it is the closest integer.Math.rint(-2.3)returns-2.0as it is the closest.Math.rint(-2.5)returns-2.0as it is the closest even integer.Math.rint(-2.7)returns-3.0as it is the closest.Math.rint(3.5)returns4.0because 4 is the closest even integer to 3.5.Math.rint(4.5)returns4.0because 4 is the closest even integer to 4.5.
Syntax of Math.rint() method
Math.rint(16.5); //returns 16.0
rint() Description
public static double rint(double x): Returns the closest double value to the argument x, this value is equal to a mathematical integer.
rint() Parameters
- x: A double value.
rint() Return value
- Closest floating point value to the argument x, which is equal to an integer.
- If the argument x is NaN (Not a number), infinity or zero, then it returns the same argument with the same sign.
Example 1
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double x = 17.5;
double x2 = -17.5;
System.out.println(Math.rint(x));
System.out.println(Math.rint(x2));
}
}
Output:
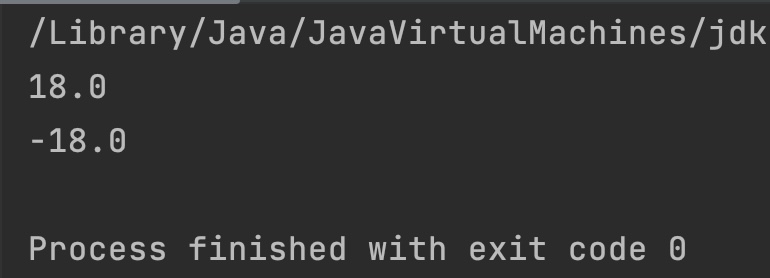
Example 2
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double x = 0;
double x2 = -5.0/0; //-ve infinity
double x3 = Double.NaN;
System.out.println(Math.rint(x));
System.out.println(Math.rint(x2));
System.out.println(Math.rint(x3));
}
}
Output:
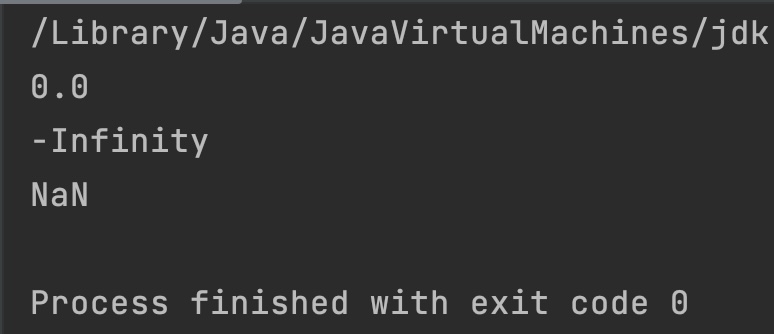
Example 3
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double x = Double.MAX_VALUE;
double x2 = Double.MIN_VALUE;
System.out.println(Math.rint(x));
System.out.println(Math.rint(x2));
}
}
Output:
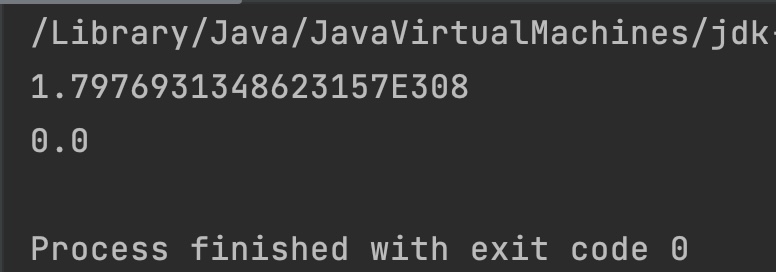
Notes:
- The
rint()method is different fromMath.round(double a)which rounds half up. I have covered the difference between these two methods here: rint vs round. - The behavior of rounding to the nearest even number when exactly halfway is known as “bankers’ rounding.”