Java Math.round() method returns closest number to the passed argument. For example, Math.round(15.75) would return 16. In this tutorial, we will discuss the round() method with examples.
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double d = 15.75;
float f = -7.6f;
// closest long value when rounding off double
System.out.println(Math.round(d));
//closest int value when rounding off float
System.out.println(Math.round(f));
}
}
Output:
16 -8
Syntax of Math.round() Method
Math.round(18.51) //returns 19
round() Description
There are two variations of round() method:
public static int round(float num): Returns closest int number.
public static long round(double num): Returns closest long number.
round() Parameters
It takes a single parameter:
- num: The number that is passed as argument.
round() Return Values
- Returns nearest int value if passed argument is float and nearest long value if passed argument is double.
- If passed argument is NaN (Not a number) then it returns 0 (zero).
- If passed float argument is negative infinity then
Integer.MIN_VALUEis returned. If passed float argument is positive infinity thenInteger.MAX_VALUEis returned. - If passed double argument is negative infinity then
Long.MIN_VALUEis returned. If passed float argument is positive infinity thenLong.MAX_VALUEis returned.
Example 1: Math.round() with float values
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
float f1 = -7.6f, f2 = 19.99f;
System.out.println(Math.round(f1));
System.out.println(Math.round(f2));
}
}
Output:

Example 2: Math.round() with double values
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
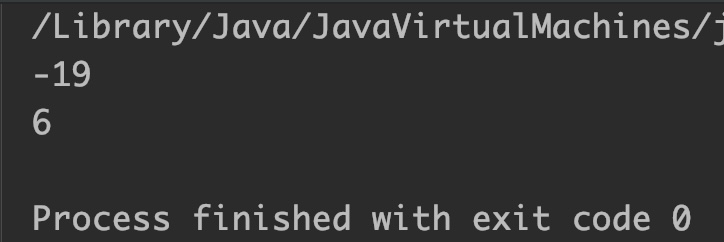
double d1 = -18.85, d2 = 6.49;
System.out.println(Math.round(d1));
System.out.println(Math.round(d2));
}
}
Output:
Example 3: Round off Positive and Negative Infinity
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
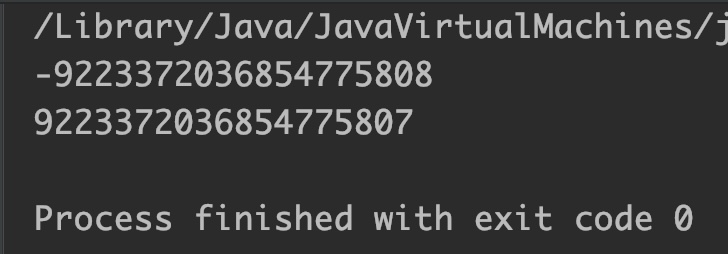
double d1 = Double.NEGATIVE_INFINITY;
double d2 = 10.0/0; //positive infinity
System.out.println(Math.round(d1)); //Long.MIN_VALUE
System.out.println(Math.round(d2)); //Long.MAX_VALUE
}
}
Output:
Example 4: Method round() with NaN
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double num = 0.0/0; //NaN (Not a Number)
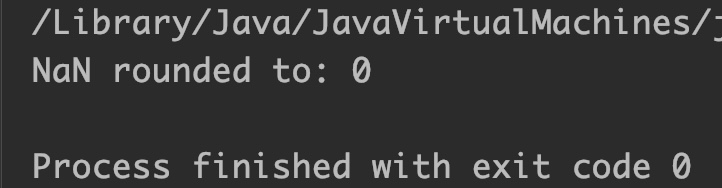
System.out.println("NaN rounded to: "+Math.round(num));
}
}
Output: