Java Math.floorDiv(int x, int y) method returns the integer quotient value after dividing argument x by argument y. This method divides the argument x by y and then applies the floor() method on the result to get the integer that is less than or equal to the original quotient value.
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x = 14;
int y= 3;
// Quotient of 14/3 is 4.67 so floor(4.67) = 4
System.out.println(Math.floorDiv(x, y));
}
}
Output:
4
Note: Do not confuse the floor() method with round() method. The round() returns the closest int value, however the floor always returns integer lower than the actual value.
Syntax of Math.floorDiv() method
Math.floorDiv(19, 4); //returns 4
floorDiv() Description
public static int floorDiv(int x, int y): Returns the floor of the quotient value, after dividing first argument x with the second argument y.
Note: The floor of a value is an integer number, which is less than or equal to the actual value.
All variations of this method:
public static int floorDiv(int x, int y) public static long floorDiv(long x, long y)
floorDiv() Parameters
- x: First argument, the dividend.
- y: Second argument, the divisor.
floorDiv() Return Value
- Returns the floor of the quotient.
- If signs of both the arguments are same, then it returns the value which is equal to what we get using / operator.
- If signs of arguments are different, then the quotient is negative. The floorDiv() returns the result less than or equal to the actual quotient value, whereas the / operator returns the result closer to zero. For example:
floorDiv(-9 , 4) == -3, whereas(-9 / 4) == -2. - It throws
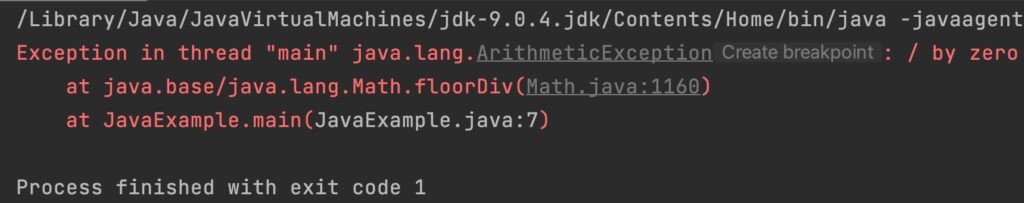
ArithmeticException, if second argument is zero.
Example 1
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x = 19;
int y= 4;
int x2 = -19;
int y2 = 4;
System.out.println(Math.floorDiv(x, y));
System.out.println(Math.floorDiv(x2, y2));
}
}
Output:

Example 2
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int y= -1;
System.out.println(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println(Math.floorDiv(x, y));
}
}
Output:

Example 3
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int y = -1;
System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println(Math.floorDiv(x, y));
}
}
Output:

Example 4
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x = 20;
int y = 0;
System.out.println(Math.floorDiv(x, y));
}
}
Output: