In this tutorial we will discuss equals() and equalsIgnoreCase() methods. Both of these methods are used for comparing two strings. The only difference between them is that the equals() methods considers the case while equalsIgnoreCase() methods ignores the case during comparison. For e.g. The equals() method would return false if we compare the strings “TEXT” and “text” however equalsIgnoreCase() would return true.
boolean equals(String str): Case sensitive comparison
boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str): Case in-sensitive comparison
Java String equals() method example
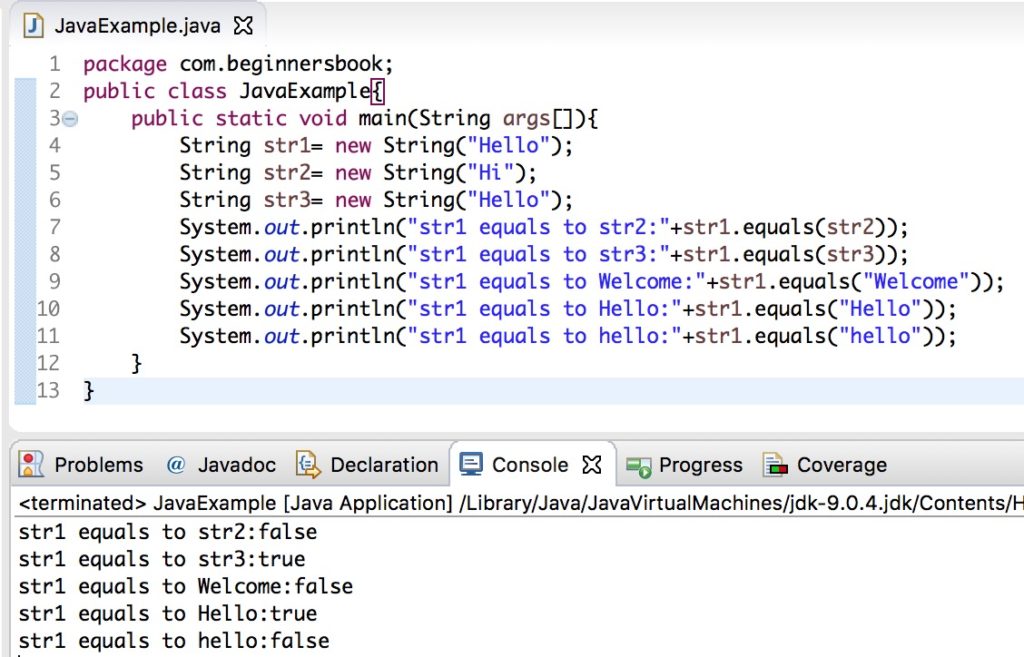
In this example we will see how equals() method works in different scenarios. We can compare two String instances (str1, str2, str3) using equals() method like we did in the following example or we can also compare string instances with the hardcoded strings passed as an argument to the equals() method as shown in the example below.
As you can observe in the output that when we compared the String str1 (value “Hello”) with the string “hello”, the equals() method returned false because this method case sensitive and considers the case while comparing strings. On the other hand the equalsIgnoreCase() method compares strings while ignoring their cases, which we will see in the next section.
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str1= new String("Hello");
String str2= new String("Hi");
String str3= new String("Hello");
System.out.println("str1 equals to str2:"+str1.equals(str2));
System.out.println("str1 equals to str3:"+str1.equals(str3));
System.out.println("str1 equals to Welcome:"+str1.equals("Welcome"));
System.out.println("str1 equals to Hello:"+str1.equals("Hello"));
System.out.println("str1 equals to hello:"+str1.equals("hello"));
}
}
Output:
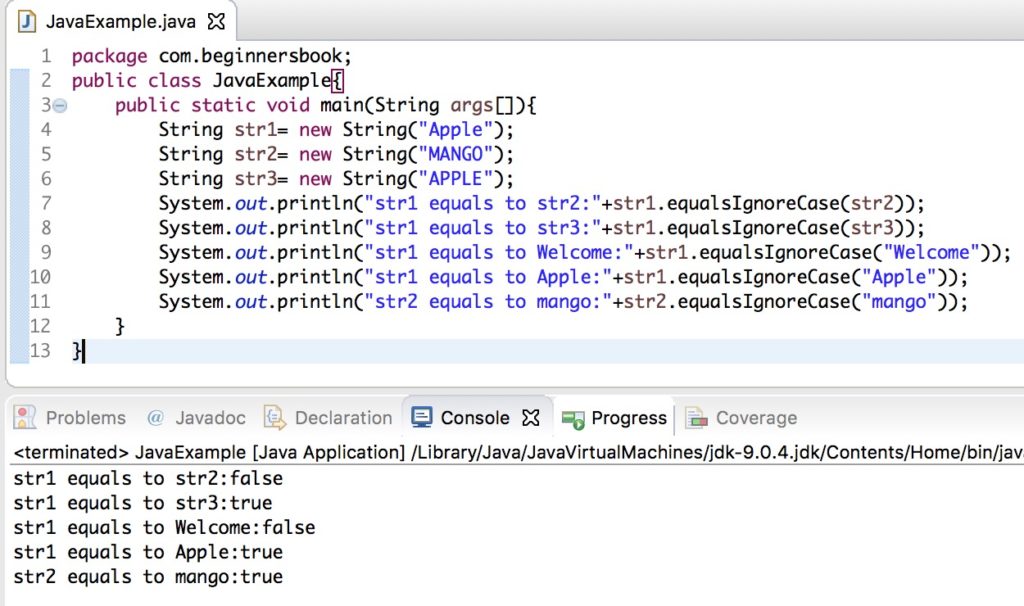
Java String equalsIgnoreCase() method example
The method equalsIgnoreCase() ignores the case while comparing two strings. In the following example we compared the string “Apple” with the string “APPLE” and it returned true.
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str1= new String("Apple");
String str2= new String("MANGO");
String str3= new String("APPLE");
System.out.println("str1 equals to str2:"+str1.equalsIgnoreCase(str2));
System.out.println("str1 equals to str3:"+str1.equalsIgnoreCase(str3));
System.out.println("str1 equals to Welcome:"+str1.equalsIgnoreCase("Welcome"));
System.out.println("str1 equals to Apple:"+str1.equalsIgnoreCase("Apple"));
System.out.println("str2 equals to mango:"+str2.equalsIgnoreCase("mango"));
}
}
Output:
Leave a Reply