Java Math.hypot(double x, double y) method returns the sqrt(x2 + y2), where x is the first argument and y is the second argument. This method doesn’t throw any exception, if there is an overflow or underflow. This means, if the result of this method is less than Double.MIN_VALUE or greater than Double.MAX_VALUE then it doesn’t throw exception.
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double x = 3;
double y = 4;
//square root of 3*3 + 4*4 == sqrt of 25
System.out.println(Math.hypot(x, y));
}
}
Output:
5.0
Syntax of Math.hypot() method
public static double hypot(double x, double y)
hypot() Description
It returns the square root of sum of squares of its arguments without overflow or underflow. The return type of this method is double.
hypot() Parameters
- x: First argument.
- y: Second argument.
hypot() Return Value
- Returns sqrt(x2 + y2) where x and y are the arguments passed to this method while calling it.
- No exception is thrown, if the result overflow or underflow the double lower and upper limit.
- If any argument is infinity, then it returns positive infinity.
- If any argument is NaN (Not a number) and the other argument is not infinity, then it returns NaN.
Example 1
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double x = 3;
double y = -4;
//square root of 3*3 + -4*-4 == sqrt of 25
System.out.println(Math.hypot(x, y));
}
}
Output:
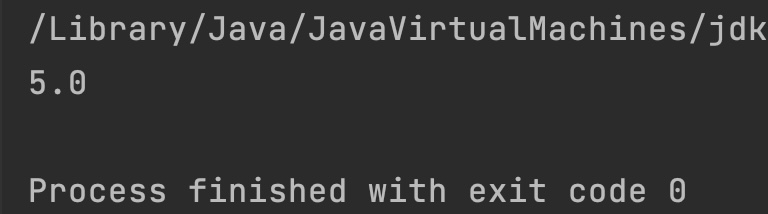
Example 2
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double x = Double.MAX_VALUE;
double y = 5;
// No exception in case of an overflow
//the returned value is equal to the MAX_VALUE
System.out.println(Math.hypot(x, y));
//to show you the MAX_VALUE printing it
System.out.println(Double.MAX_VALUE);
}
}
Output:

Example 3
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double x = Double.MIN_VALUE;
double y = 0;
// No exception in case of an underflow
//the returned value is equal to the MIN_VALUE
System.out.println(Math.hypot(x, y));
System.out.println(Double.MIN_VALUE);
}
}
Output:
