Java Math.pow() method returns, first argument raised to the power of second argument. For example, Math.pow(3, 2) returns 9. In this tutorial, we will discuss pow() method with examples.
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double num = 3, num2 = 2;
//3 raised to the power 2 == 3*3 == 9
System.out.println(Math.pow(num, num2));
}
}
Output:
9.0
Syntax of Math.pow() method
Math.pow(4, 2); //returns 16.0
pow() Description
public static double pow(double a, double b): It returns the value of a raised to the power b.
pow() Parameters
It takes two parameters:
- a: First argument, the base.
- b: Second argument, the exponent.
pow() Return Values
- Returns a to the power b: ab.
- If the second argument is 1 then it returns the first argument as output.
- If the second argument is zero of any sign, it returns 1.0 as output.
- If the first or second argument is NaN then it returns NaN (Not a Number).
- If first argument is finite & less than zero and second argument is not an integer then NaN is returned.
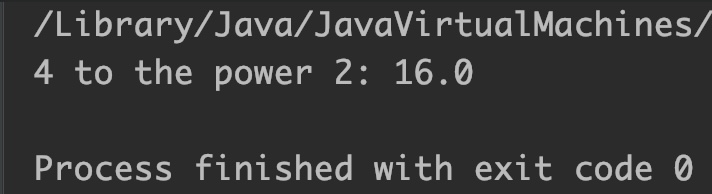
Example 1: Finding power using Math.pow()
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double num = 4, num2 = 2;
//4 raised to the power 2 == 4*4 == 16
System.out.println("4 to the power 2: "+Math.pow(num, num2));
}
}
Output:
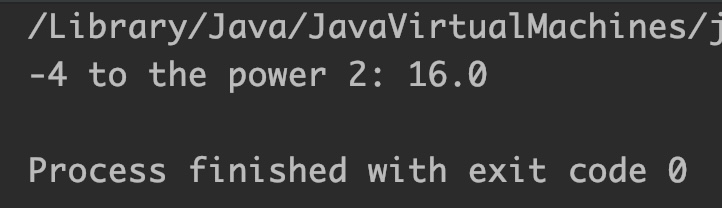
Example 2: Power of a negative number (Base is negative)
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double num = -4, num2 = 2;
//-4 raised to the power 2 == -4 * -4 == 16
System.out.println("-4 to the power 2: "+Math.pow(num, num2));
}
}
Output:
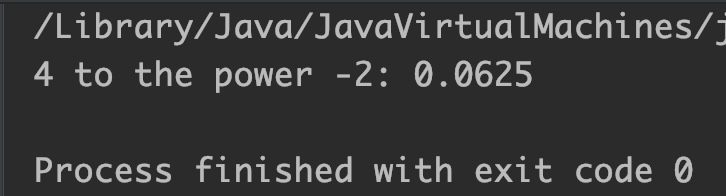
Example 3: If exponent is negative
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double num = 4, num2 = -2;
//4 raised to the power -2 == 1/4 * 1/4 == 1/16
System.out.println("4 to the power -2: "+Math.pow(num, num2));
}
}
Output:
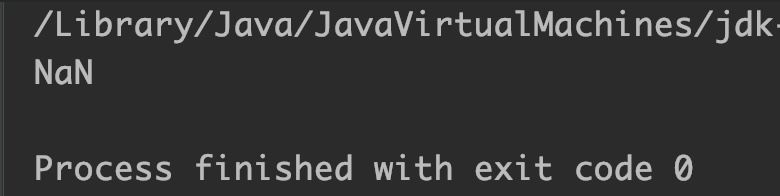
Example 4: Base negative and exponent is not an integer
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double num = -10, num2 = .2;
// If first argument is finite and less than zero and
// second argument is not an integer then result is NaN
System.out.println(Math.pow(num, num2));
}
}
Output: