Java Math.ulp() method returns distance between the number passed as argument and the next floating point number. An ulp (unit in the last place or unit of least precision) is the distance between two consecutive floating point numbers.
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double d = 0.99;
System.out.println(Math.ulp(d));
}
}
Output:
1.1102230246251565E-16
Syntax of Math.ulp() method
public static double ulp(double d) public static float ulp(float f)
ulp() Description
For argument d: It returns the positive distance between argument d and next floating point double value, which is larger in magnitude.
For argument f: It returns the positive distance between argument f and next floating point float value which is larger in magnitude than the argument.
ulp() Parameters
- d: A double value whose ulp is to be determined.
- f: A float value whose ulp is to be determined.
ulp() Return Value
- Size of an ulp of the argument.
- For non-NaN argument
x, theulp(-x) == ulp(x). - If the argument is NaN (Not a number), then it returns NaN.
- If the argument is positive or negative infinity, then it returns positive infinity.
- If the argument
dis positive or negative zero, then it returns Double.MIN_VALUE. - If the argument
fis positive or negative zero, then it returns Float.MIN_VALUE. - If the argument
dis +or- Double.MAX_VALUE, then it returns 2971. - If the argument
fis +or- Float.MAX_VALUE, then it returns 2104.
Example 1
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double d = -5.99;
double d2 = 5.99;
System.out.println(Math.ulp(d));
System.out.println(Math.ulp(d2));
}
}
Output:

Example 2
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
float f = Float.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
System.out.println(Math.ulp(f));
}
}
Output:
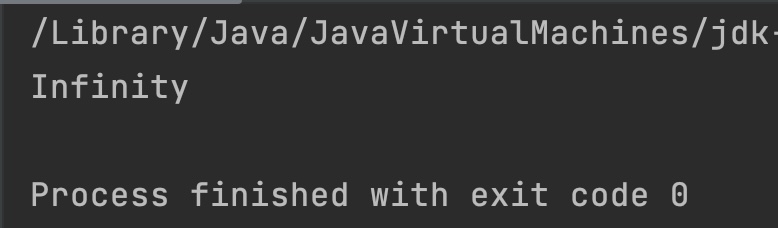
Example 3
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double d = Double.MAX_VALUE;
float f = Float.MAX_VALUE;
System.out.println(Math.ulp(d));
System.out.println(Math.ulp(f));
}
}
Output:

Example 4
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double d = -0.0;
float f = 0.0f;
System.out.println(Math.ulp(d));
System.out.println(Math.ulp(f));
}
}
Output:
