Java Math.IEEEremainder(double f1, double f2) method returns the remainder of f1/f2 based on the IEEE 754 standard. The remainder is equal to the f1 - f2 * n, where f1 and f2 are the arguments and n is an integer closest to the quotient of f1/f2. If two integers are equally close to the quotient then n is the integer which is even.
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double f1 = 22.0;
double f2 = 4.0;
// quotient is 5.5, n is chosen as 6 (even)
// f1 - f2*n == 22 - 4*n == 22 - 24 == -2
System.out.println(Math.IEEEremainder(f1, f2));
}
}
Output:
-2.0
Syntax of Math.IEEEremainder() method
public static double IEEEremainder(double f1, double f2)
IEEEremainder() Description
It returns IEEE remainder defined as f1 - f2*n, n is the closest integer to the quotient of division operation of f1 and f2.
IEEEremainder() Parameters
- f1: First argument, the dividend.
- f2: Second argument, the divisor.
IEEEremainder() Return Value
- Remainder of two arguments calculated based on this formula:
f1 - f2*n. - If the remainder is zero, then the sign of it is same as the first argument
f1. - If any argument is NaN (Not a number) or the first argument is infinite or the second argument is zero, then it returns NaN.
- If the first argument is finite and the second argument is infinite, then it returns the first argument as a result.
Example 1
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double f1 = 20.0;
double f2 = -4.0;
// remainder is zero, sign is same as first argument
System.out.println(Math.IEEEremainder(f1, f2));
}
}
Output:

Example 2
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
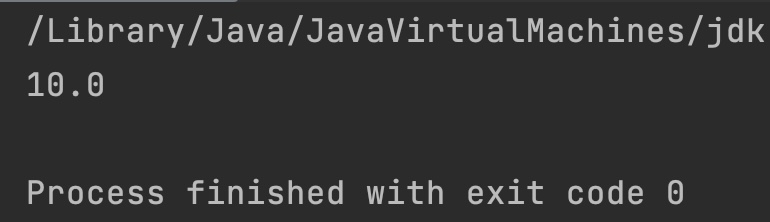
double f1 = 10.0;
double f2 = 3.0;
// quotient is 3.33 so n is 3
// f1 - f2*n == 10 - 3*3 == 1
System.out.println(Math.IEEEremainder(f1, f2));
}
}
Output:
Example 3
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
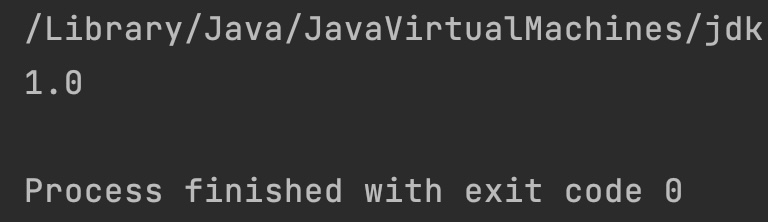
double f1 = 10.0;
double f2 = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
// first argument is finite and second is infinite
// output is the first argument
System.out.println(Math.IEEEremainder(f1, f2));
}
}
Output:
Example 4
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
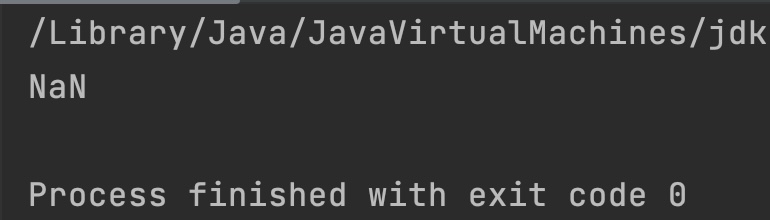
double f1 = 0.0/0; //NaN
double f2 = 5;
// any argument is NaN, result is NaN
System.out.println(Math.IEEEremainder(f1, f2));
}
}
Output: