The compareTo() method compares this Integer with the Integer argument. It returns, 0 if this Integer is equal to given Integer, a value less than 0 if this Integer is less than Integer argument, a value greater than zero if this Integer is greater than Integer argument. This is a signed comparison.
Hierarchy:
java.lang Package
-> Integer Class
-> compareTo() Method
Syntax of compareTo() method
public int compareTo(Integer anotherInteger)
compareTo() Parameters
anotherInteger– The Integer which needs to be compared to this Integer.
compareTo() Return Value
It returns:
- 0, if this Integer is equal to
anotherInteger. - a value less zero, if this Integer is less than
anotherInteger. - a value greater than zero, if this Integer is greater than
anotherInteger.
Supported java versions: Java 1.2 and onwards
Example 1
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String[] args){
Integer obj = new Integer(55);
int result = obj.compareTo(34);
int result2 = obj.compareTo(55);
int result3 = obj.compareTo(89);
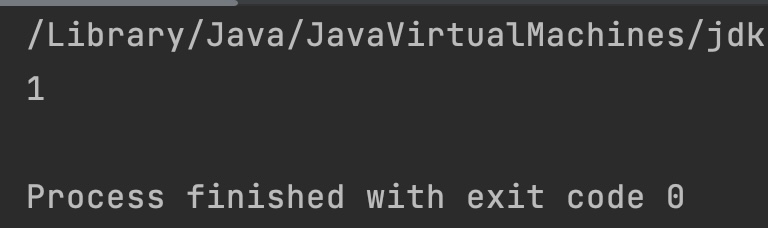
System.out.println(result); //55 > 34 so 1
System.out.println(result2); //55 == 55 so 0
System.out.println(result3); // 55 < 89 so -1
}
}
Output:
Example 2
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String[] args){
Integer obj = new Integer(11);
Integer obj2 = new Integer(22);
//Comparing two Integer objects
int result = obj.compareTo(obj2);
int result2 = obj2.compareTo(obj);
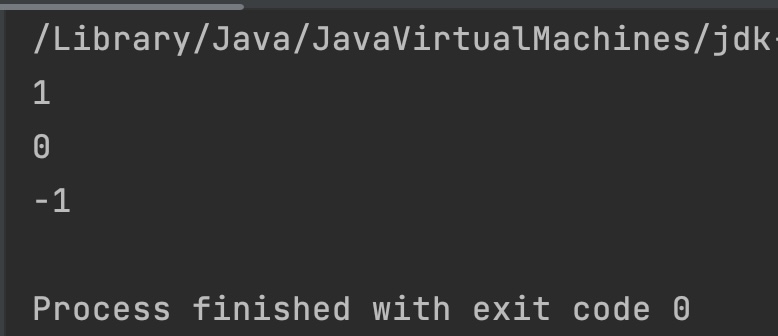
System.out.println(result); //11 < 22 so -1
System.out.println(result2); //22 > 11 so 1
}
}
Output:
Example 3
This method takes sign into consideration while comparing two integers numerically.
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String[] args){
//integer values given as strings, we can
// use Integer class constructor that accepts
//string values and return Integer object
Integer obj = new Integer("101");
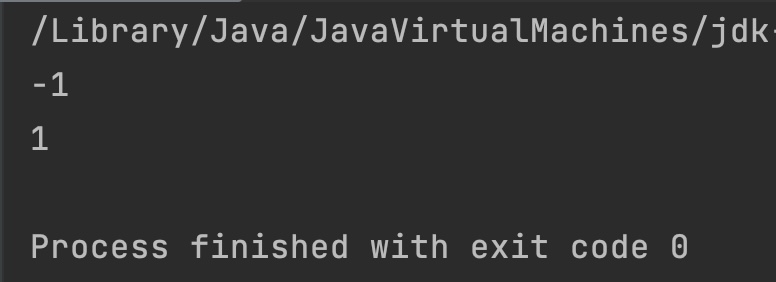
Integer obj2 = new Integer("-5500"); //-5500 < 101
System.out.println(obj.compareTo(obj2));
}
}
Output: