The Java String compareTo() method is used for comparing two strings lexicographically. Each character of both the strings is converted into a Unicode value for comparison. If both the strings are equal then this method returns 0 else it returns positive or negative value. The result is positive if the first string is lexicographically greater than the second string else the result would be negative.
Syntax of compareTo() method
int compareTo(String str)
This method takes string as an argument and returns an integer. It returns positive number, negative number or zero based on the comparison:
- str1.compareTo(str2) returns positive number, if str1 > str2
- str1.compareTo(str2) returns negative number, if str1 < str2
- str1.compareTo(str2) returns 0, if str1 = str2
For example:
"hello".compareTo("hello") // returns 0
"hello".compareTo("Hello") //returns 32
"Hello".compareTo("hello") //returns -32
Java String compareTo() method Example
Here we have three Strings and we are comparing them with each other using compareTo() method.
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str1 = "String method tutorial";
String str2 = "compareTo method example";
String str3 = "String method tutorial";
int var1 = str1.compareTo(str2);
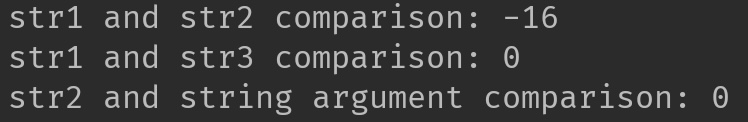
System.out.println("str1 and str2 comparison: "+var1);
int var2 = str1.compareTo(str3);
System.out.println("str1 and str3 comparison: "+var2);
int var3 = str2.compareTo("compareTo method example");
System.out.println("str2 and string argument comparison: "+var3);
}
}
Output:
How to find length of a string using String compareTo() method
Here we will see an interesting example of how to use the compareTo() method to find the length of a string. If we compare a string with an empty string using the compareTo() method then the method would return the length of the non-empty string.
For example:
String str1 = "Negan"; String str2 = ""; //empty string //it would return the length of str1 in positive number str1.compareTo(str2); // 5 //it would return the length of str1 in negative number str2.compareTo(str1); //-5
In the above code snippet, the second compareTo() statement returned the length in negative number, this is because we have compared the empty string with str1 while in first compareTo() statement, we have compared str1 with empty string.
Lets see the complete example:
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str1 = "Cow";
//This is an empty string
String str2 = "";
String str3 = "Goat";
int lenOfStr1 = str1.compareTo(str2);
int lenOfStr3 = str3.compareTo(str2);
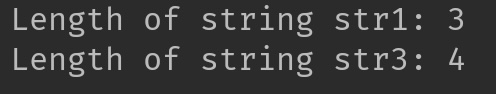
System.out.println("Length of string str1: "+lenOfStr1);
System.out.println("Length of string str3: "+lenOfStr3);
}
}
Output:
Is Java String compareTo() method case sensitive?
Yes, compareTo() method is case sensitive. The output of "HELLO".compareTo("hello") would not be zero. In the following example, we will compare two strings using compareTo() method. Both the strings are same, however one of the string is in uppercase and the other string is in lowercase.
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
//uppercase
String str1 = "HELLO";
//lowercase
String str2 = "hello";;
System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str2));
}
}
Output:
-32
As you can see that the output is not zero, which means that compareTo() method is case sensitive. However we do have compareToIgnoreCase() method that ignores the case while comparing two strings.
Exceptions in compareTo() method
The following exceptions can occur while using compareTo() method:
1. NullPointerException
2. ClassCastException
NullPointerException
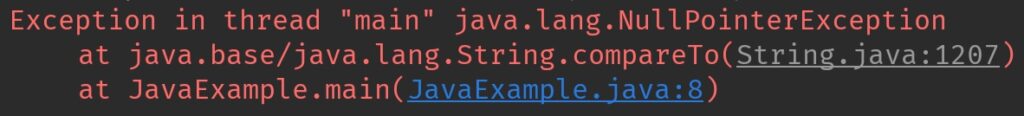
This method throws NullPointerException, if it is used on a string that contains null value.
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str = "Java is Awesome!";
//references to null
String str2 = null;
System.out.println(str.compareTo(str2));
}
}
Output:
Sangbeet says
If both the strings has space in them?
Also if the no of characters in both the strings are not equal then what will be the output?
Andy L. says
I think a better description of what this method does is that it compares the FIRST character that is not equal in both strings. Anything after that will NOT be compared, whether one string has more or less characters are equal or not. The interger given in the result is based on the difference in value of the characters in the ASCII chart.
This would apply for the space as well. If space is placed as the first distinct character in the two strings, then it would be compared depending the ASCII values of the two characters.
For example, if you compared a space character (which has a ASCII value of 32) to a comma (which has an ASCII value of 44) using the compareTo() method, assuming that they are the first distinct chracters found in the two strings, then the result would be the difference between 32 and 44, which is -12.