In this tutorial, we will see how to take input from user in Kotlin.
Example 1: Display String entered by user
In this example, we will take the input from user and display it in the output. Here we are using readLine() function to read the string entered on console.
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
print("Write anything here: ")
val enteredString = readLine()
println("You have entered this: $enteredString")
}
Output:
Write anything here: welcome to beginnersbook.com You have entered this: welcome to beginnersbook.com
Example 2: Taking input and converting it into a different type
As we have seen in the above example that the readLine() function reads the input as a String. If we want to take the input in a different type such as integer, long, double then we need to either explicitly convert the input to another type or use the java Scanner class.
Taking the input as String and converting it to an int
Here we are explicitly converting the input to an integer number.
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
print("Write any number: ")
val number = Integer.valueOf(readLine())
println("The entered number is: $number")
}
Output:
Write any number: 101 The entered number is: 101
Taking the input other than String using Scanner class
In this example we are taking the input as an integer and float using the nextInt() and nextFloat() functions respectively. Similarly we can use nextLong(), nextDouble() and nextBoolean() methods to take long, double and boolean inputs respectively.
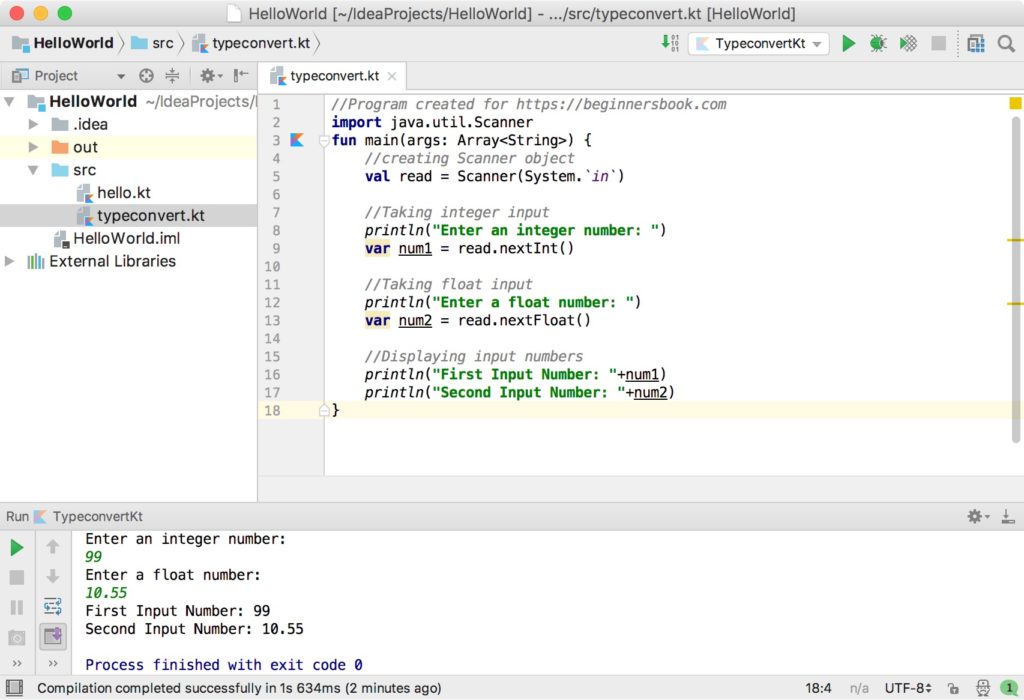
//Program created for https://beginnersbook.com
import java.util.Scanner
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
//creating Scanner object
val read = Scanner(System.`in`)
//Taking integer input
println("Enter an integer number: ")
var num1 = read.nextInt()
//Taking float input
println("Enter a float number: ")
var num2 = read.nextFloat()
//Displaying input numbers
println("First Input Number: "+num1)
println("Second Input Number: "+num2)
}
Output:
Enter an integer number: 99 Enter a float number: 10.55 First Input Number: 99 Second Input Number: 10.55
Leave a Reply