The continue construct skips the current iteration of the loop and jumps the control to end of the loop for the next iteration. The continue is usually used with if else expression to skip the current iteration of the loop for a specified condition. In this guide, we will lean Continue construct and Continue Labels.
Kotlin Continue For loop Example
fun main(args : Array<String>){
for (n in 1..5){
println("before continue, Loop: $n")
if(n==2||n==4)
continue
println("after continue, Loop: $n")
}
}
Output:
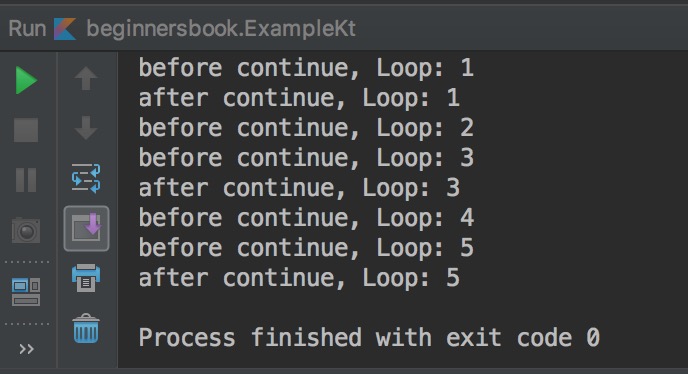
As you can see in the output that println("after continue, Loop: $n") statement didn’t execute for the loop iterations n==2 and n==4 because on these iterations we have used the continue before this statement which skipped the iteration for these values of n.
However you can observe that println("before continue, Loop: $n") statement executed on every iteration because it is executed before Continue is encountered.
Based on this you can conclude that continue skips the iteration but it is not capable of skipping the statements that are encountered before continue. As soon as continue is encountered, the control jumps to the end of the loop skipping the rest of the statements.
Lets take another example
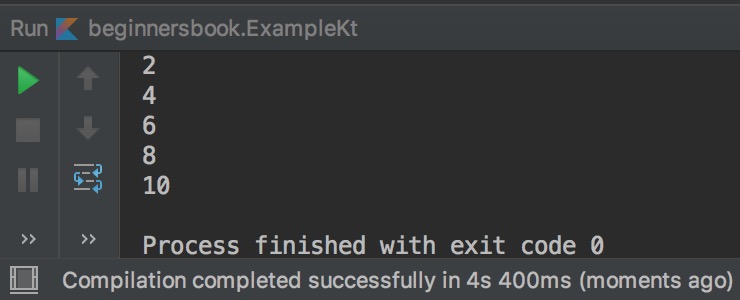
Kotlin continue example: displaying even numbers
fun main(args : Array<String>){
for (n in 1..10){
if(n%2!=0)
continue
println("$n")
}
}
Output:
Continue Label
Till now we have learned how continue works. Lets learn about continue labels. These labels are cool basically they give us more control when we are dealing with nested loops.
Lets take an example where we first do not use continue label and then we will take the same example with continue label.
Nested loop example without continue label
In this example we have a nested for loop and we are not using label. When we do not use labels we do not have any control and as soon as the continue is encountered the current iteration is skipped for the inner loop.
fun main(args : Array<String>){
for (x in 'A'..'D'){
for (n in 1..4){
if (n==2||n==4)
continue
println("$x and $n")
}
}
}
Output:
A and 1 A and 3 B and 1 B and 3 C and 1 C and 3 D and 1 D and 3
Nested loop example with continue label
You can see in the above example output that for n value 2 and 4 the iteration is skipped for the inner loop. Lets say we want to skip the iteration for the outer for loop, we can do so with the help of continue labels.
fun main(args : Array<String>){
myloop@ for (x in 'A'..'D'){
for (n in 1..4){
if (n==2||n==4)
continue@myloop
println("$x and $n")
}
}
}
Output:
A and 1 B and 1 C and 1 D and 1
Basically what happened here is that as soon as the n value reached 2 the control jumped to the end of outer loop because of the label and it happened for the each iteration. The syntax of the continue label is pretty straight forward as you just have to give a name to label followed by @ symbol and the same name needs to be appended with the continue statement as shown in the above example.
Leave a Reply