The break statement is used to terminate the loop immediately without evaluating the loop condition. As soon as the break statement is encountered inside a loop, the loop terminates immediately without executing the rest of the statements following break statement. In this guide, we will learn how break works and we will also discuss break labels.
Kotlin break example
The break statement is usually used with if else expression.
fun main(args : Array<String>){
for(n in 1..10){
println("before break, Loop: $n")
if (n==5) {
println("I am terminating loop")
break
}
}
}
Output:
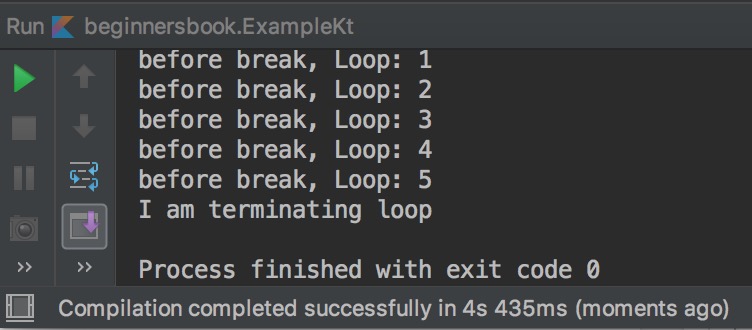
As you can observe in the output that as soon as the break is encountered the loop terminated.
Kotlin break example in nested loop
When break is used in the nested loop, it terminates the inner loop when it is encountered.
fun main(args : Array<String>){
for(ch in 'A'..'C'){
for (n in 1..4){
println("$ch and $n")
if(n==2)
break
}
}
}
Output:
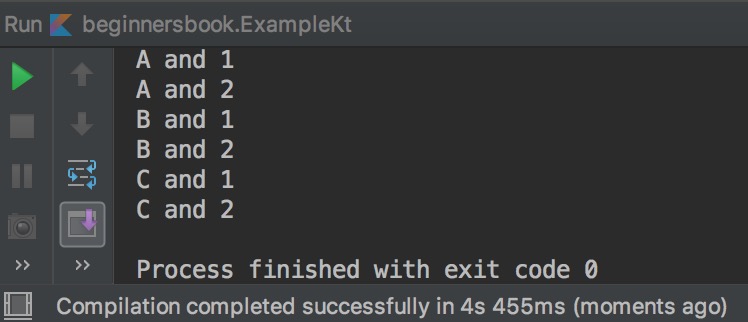
As you can observe in the output that the outer loop never got terminated, however the inner loop got terminated 3 times.
Kotlin break labels
Lets talk about labels now. Similar to continue labels, the break label gives us more control over which loop is to be terminated when the break is encountered.
In the above example of nested loop, the inner loop got terminated when break encountered. Lets write a program with the help of labels to terminate the outer loop rather than inner loop.
fun main(args : Array<String>){
myloop@ for(ch in 'A'..'C'){
for (n in 1..4){
println("$ch and $n")
if(n==2)
break@myloop
}
}
}
Output:
A and 1 A and 2
The syntax of label is simple we just have to use any name followed by @ in front of the loop which we want to terminate and the same name needs to be appended with the break keyword prefixed with @ as shown in the above example.
Leave a Reply