An abstract class cannot be instantiated, which means we cannot create the object of an abstract class. Unlike other class, an abstract class is always open so we do not need to use the open keyword.
Points to Note:
1. We cannot create the object of an abstract class.
2. Property and member function of an abstract class are by default non-abstract. If you want to override these in the child class then you need to use open keyword for them.
3. If a member function is abstract then it must be implemented in the child class. An abstract member function doesn’t have a body only method signature, the implementation is done in the child class.
Abstract class Example
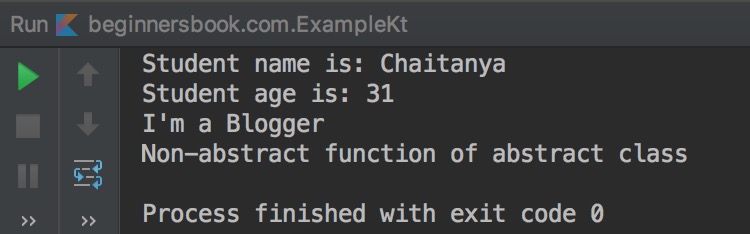
In the following example we have an abstract class Student, we cannot create an object of this class. However we can inherit this class, like we did in the following example. Class College inherits abstract class Student.
The function func() is an abstract function which means it doesn’t have a body and only method signature, however since it is an abstract function, it must be overriden in the child class.
abstract class Student(name: String, age: Int) {
init {
println("Student name is: $name")
println("Student age is: $age")
}
//non-abstract function
fun demo() {
println("Non-abstract function of abstract class")
}
//abstract function
abstract fun func(message: String)
}
class College(name: String, age: Int): Student(name, age) {
override fun func(message: String) {
println(message)
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val obj = College("Chaitanya", 31)
obj.func("I'm a Blogger")
obj.demo()
}
Output:
Leave a Reply