In this guide, we will learn about interfaces. Similar to an abstract class, an interface cannot be instantiated because it doesn’t have any constructor.
Points to Note:
1. An interface can have both abstract and non-abstract function.
2. An interface can only have abstract property (data member), non-abstract properties are not allowed.
3. A class can implement more than one interfaces.
4. All abstract properties and abstract member functions of an interface must be overriden in the classes that implement it.
Kotlin Interfaces Example
In the following example, we have an interface MyInterface which contains a non-abstract method func and abstract property str & abstract function demo.
interface MyInterface{
var str: String
fun demo()
fun func(){
println("Hello")
}
}
class MyClass: MyInterface{
override var str: String = "BeginnersBook.com"
override fun demo() {
println("demo function")
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val obj = MyClass()
obj.demo()
obj.func()
println(obj.str)
}
Output:
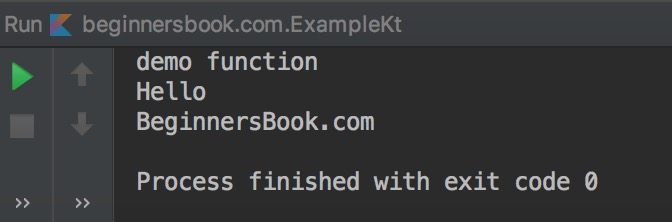
Kotlin – Implementing more than one interfaces
In the following example, we have two interfaces X and Y. The class MyClass implements both the interfaces X and Y. The class gives implementation to both the abstract methods of interfaces X and Y.
interface X {
fun demoX() {
println("demoX function")
}
fun funcX()
}
interface Y {
fun demoY() {
println("demoY function")
}
fun funcY()
}
// This class implements X and Y interfaces
class MyClass: X, Y {
override fun funcX() {
println("Hello")
}
override fun funcY() {
println("Hi")
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val obj = MyClass()
obj.demoX()
obj.demoY()
obj.funcX()
obj.funcY()
}
Output:
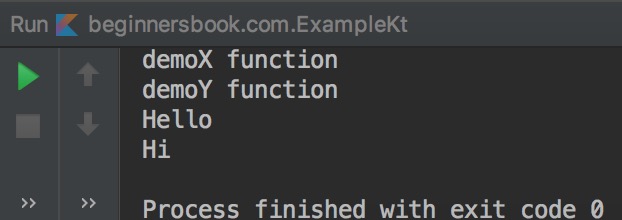
When multiple interfaces have same method name
In the following example we have two interfaces X and Y however both these interfaces have same function demo(). The class MyClass implements both these interfaces, now when we try to call this function demo() using the object of class then we will get compilation error because compiler is confused which method to call.
interface X {
fun demo() {
println("demoX function")
}
}
interface Y {
fun demo() {
println("demoY function")
}
}
// This class implements X and Y interfaces
class MyClass: X, Y
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val obj = MyClass()
obj.demo()
}
How to resolve the conflict of same method name
To resolve the above conflict we have overridden the method in the class, which was previously causing the conflict. In the overriden method, we specified exactly which method to call using super keyword. In the following example we wanted to call the demo() method of interface Y so we have specified super<Y>.demo() in the overriden method.
interface X {
fun demo() {
println("demoX function")
}
}
interface Y {
fun demo() {
println("demoY function")
}
}
// This class implements X and Y interfaces
class MyClass: X, Y{
override fun demo() {
super<Y>.demo()
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val obj = MyClass()
obj.demo()
}
Output:
demoY function
Tanishk Tripathi says
Undoubtedly one of the best websites to learn Java and Kotlin without any assistance.
Articles on this website are so clear that after reading them there’s hardly any chance of getting any doubt.
Thank you Chaitanya sir for all the hardwork !