StringBuilder in Java is used to create mutable strings. A mutable string is the one which can be modified instead of creating new string instance. StringBuilder is an alternative to Java String class. In this guide, we will discuss StringBuilder class in detail. We will also cover important methods of Java StringBuilder class with examples.
Why we need StringBuilder when we can use Strings?
As we discussed previously that strings are immutable, which means the methods that operate on strings cannot change the value of strings, instead a new memory is allocated every time. For example, when performing string concatenation using += operator, a new memory is allocated to store the concatenated string.
On the other hand, StringBuilder is immutable. When strings are concatenated using StringBuilder, this class checks if the existing array of characters can be updated to store the concatenated string. It only requires new memory when the concatenated string is larger than the already allocated buffer to the StringBuilder instance.
Constructors of StringBuilder class
| Constructor | Description |
| StringBuilder() | This is the base constructor of the StringBuilder class, it creates an empty StringBuilder instance with the initial capacity of 16. |
| StringBuilder(String str) | This creates a StringBuilder instance with the specified string. |
| StringBuilder(int capacity) | In this constructor, we pass an integer number. This creates StringBuilder instance with the specified capacity instead of the default capacity 16. |
| StringBuilder(CharSequence charSeq) | This Creates a StringBuilder instance with the specified character sequence. |
Let’s see an example of StringBuilder class constructors:
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
//creating StringBuilder using default constructor
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
//appending a string to newly created instance
sb.append("BeginnersBook.com");
System.out.println("First String: "+sb);
//Using StringBuilder(String str) constructor
String str = "hello";
StringBuilder sb2 = new StringBuilder(str);
System.out.println("Second String: "+sb2);
//Using StringBuilder(int Capacity) constructor
StringBuilder sb3 = new StringBuilder(24);
System.out.println("Capacity of sb3: "+sb3.capacity());
//creating StringBuilder(CharSequence charSeq) constructor
StringBuilder sb4 = new StringBuilder("Welcome");
System.out.println("Fourth String: "+sb4);
}
}
Output:

Methods of StringBuilder in Java
| Method Signature | Description |
| StringBuilder append (String str) | This method appends (concatenates) the specified string str to the already existing StringBuilder value. |
| StringBuilder insert (int pos, String str) | It inserts the specified string str at the specified position pos. |
| StringBuilder replace(int startIndex, int endIndex, String str) | It replaces the string between the specified startIndex and endIndex with the specified string str. |
| StringBuilder delete(int startIndex, int endIndex) | It deletes a portion of the string from the specified startIndex till endIndex. |
| StringBuilder reverse() | It is used to reverse the given string. |
| int capacity() | It prints the current capacity of the StringBuilder instance |
| void ensureCapacity(int minElements) | It increases the capacity of the StringBuilder to ensure that it can hold at least the mentioned minElements. |
| char charAt(int index) | Returns the character |
| int length() | Returns the length of the current string. |
| String substring(int startIndex) | Returns substring starting from the specified startIndex. |
| String substring(int startIndex, int endIndex) | Returns substring starting from the specified startIndex till specified endIndex. |
| int indexOf(String subStr) | It returns the index of first occurrence of the specified substring subStr in the given string. |
| int lastIndexOf(String str) | It returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified substring subStr in the given string. |
| void trimToSize() | It attempts to trim the free size of the StringBuilder if possible. |
| int offsetByCodePoints(int index, int codePointOffset) | The offsetByCodePoints(int index, int codePointOffset) method returns the index of a character that is offset from the given index by the specified code points. |
Java StringBuilder Examples
Example 1: Insert at position using insert() method
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
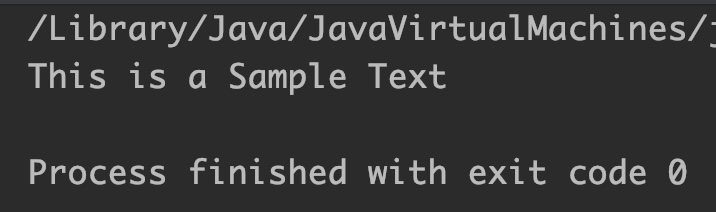
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("This is Text");
//insert "a Sample" string after "is"
//index starts with 0 so the index of s is 6
sb.insert(7, " a Sample");
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
Output:
Example 2: StringBuilder append() method
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
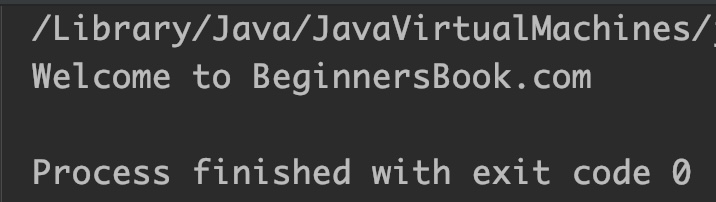
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Welcome to");
//appending specified string at the end of given string
sb.append(" BeginnersBook.com");
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
Output:
Example 3: StringBuilder replace() method
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
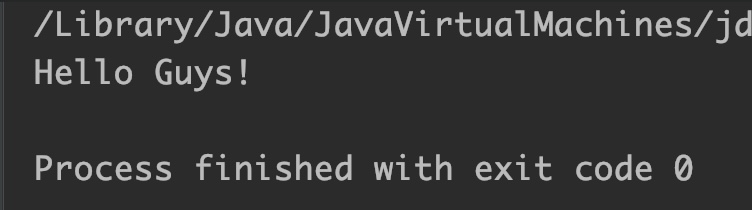
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder("Hi Guys!");
//replace "Hi" with "Hello"
sb.replace(0,2,"Hello");
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
Output:
Example 4: StringBuilder reverse() method
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
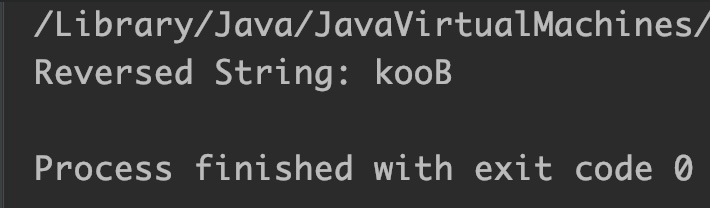
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder("Book");
//reverses the string "Book"
sb.reverse();
System.out.println("Reversed String: "+sb);
}
}
Output:
Example 5: StringBuilder delete() method
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder("BeginnersBook");
//delete substring "Beginners"
sb.delete(0, 9);
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
Output:
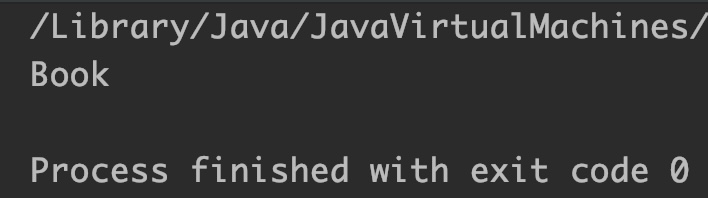
Example 6: StringBuilder capacity() method
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
//default capacity 16
System.out.println("Current Capacity: "+sb.capacity());
//appended string is 13 chars, can be adjusted in current
//capacity so no capacity increase
sb.append("BeginnersBook");
System.out.println("Current Capacity: "+sb.capacity());
//Need to increase capacity to append
//this string. (16*2) +2 = 34
sb.append("Book");
System.out.println("Current Capacity: "+sb.capacity()); //34
}
}
Output:
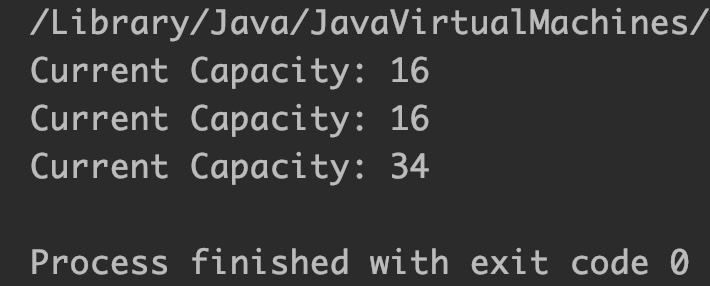
Example 7: StringBuilder length() method
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
sb.append("Welcome");
System.out.println("Length of string: "+sb.length());
}
}
Output:
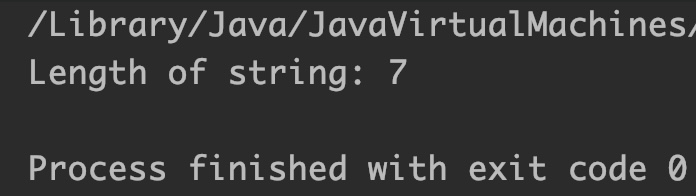
Example 8: StringBuilder indexOf() method
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
sb.append("Welcome");
System.out.println("String: "+sb);
System.out.println("Index of substring come: "+sb.indexOf("come"));
}
}
Output:
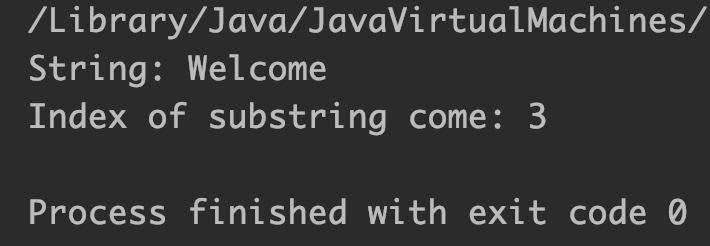
Example 9: StringBuilder charAt() method
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
sb.append("Welcome");
System.out.println("String: "+sb);
System.out.println("Char at index 3 is: "+sb.charAt(3));
}
}
Output:
Conclusion
In this guide, we learned how StringBuilder class is different from the Java String class. We have discussed methods of Java StringBuilder class with examples. You can head over to our Java tutorial for beginners section to start learning other such concepts in detail.