Java StringBuffer toString() method returns the string representation of this character sequence. An object of StringBuffer class represents a character sequence. The toString() method converts this sequence into a String.
Syntax of toString() method
String str = sb.toString(); //converts sb to a String str Here, sb is an object of StringBuffer class
toString() Description
public string toString(): Returns a String representation of the StringBuffer sequence.
toString() Parameters
- It does not take any parameter.
toString() Return Value
- It returns a string that is equivalent to the char sequence represented by the object of StringBuffer class.
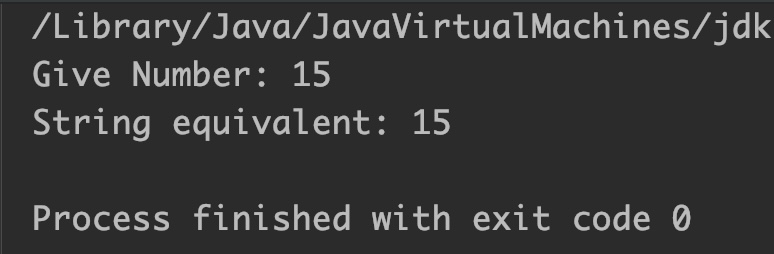
Example 1: Convert int value to String using toString()
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
int num = 15; //int value
sb.append(num); //append integer to sb
System.out.println("Give Number: "+num);
String str = sb.toString(); //convert sb to string
System.out.println("String equivalent: "+str);
}
}
Output:
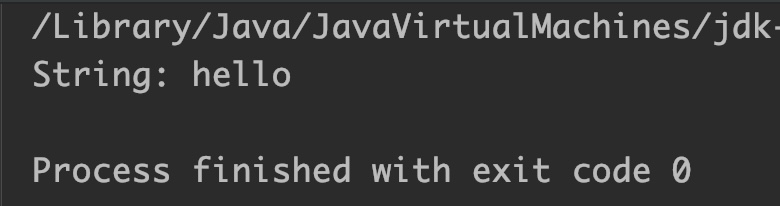
Example 2: Convert char array to String using toString()
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
//char array
char[] ch = {'h','e','l','l','o'};
//append array to StringBuffer
sb.append(ch);
//convert StringBuffer to String
String str = sb.toString();
System.out.println("String: "+str);
}
}
Output:
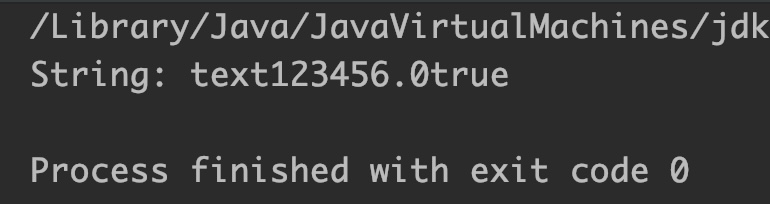
Example 3: Append multiple data types and convert it into String
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
char[] ch = {'t','e','x','t'};//char array
double num = 123456;//double value
boolean b = true;//boolean value
sb.append(ch); //append char array
sb.append(num); //append double
sb.append(b); //append boolean
//convert StringBuffer instance to String
String str = sb.toString();
System.out.println("String: "+str);
}
}
Output: