Java StringBuilder delete() method is used to delete a portion of the string. A StringBuilder instance represents a character sequence. We can delete a portion of this char sequence, by specifying start and end index in delete() method.
The syntax of delete() method is:
//deletes a substring from first char till 5th char sb.delete(0, 5); //end index is exclusive //deletes a substring from 2nd char till 4th char sb.delete(1, 4);
Here, sb is an object of StringBuilder class.
delete() Description
public StringBuilder delete(int start, int end): It deletes a substring from this StringBuilder instance from start index till end index.
This method throws StringOutOfBoundsException, if any of the following condition occurs:
- If indexes are negative.
- If any of the index is greater than or equal to the length.
- if start index > end index.
delete() Parameters
The delete() method of Java StringBuilder class takes a two parameters:
- start: It represents the starting index, deletion starts from here. It is inclusive.
- end: It represents the end index, deletion end here. It is exclusive.
delete() Return Value
- It returns a new StringBuilder object containing the resultant string (char sequence ) after deletion.
Example 1: Deleting a Substring
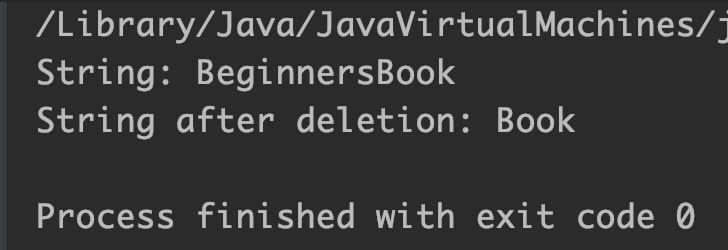
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("BeginnersBook");
System.out.println("String: "+sb);
//deleting the substring "Beginners"
sb = sb.delete(0, 9);
System.out.println("String after deletion: "+sb);
}
}
Output:
Example 2: When both start and end index are equal
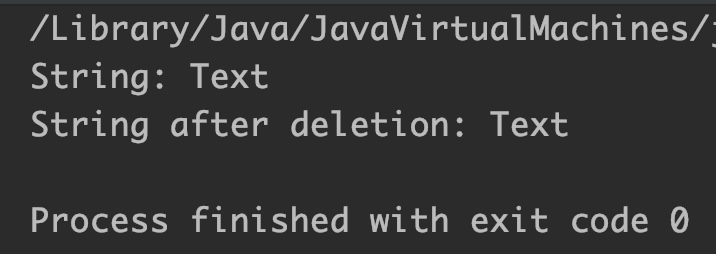
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Text");
System.out.println("String: "+sb);
//start and end index are equal
//nothing will happen as start index is inclusive and
//end index is exclusive
sb = sb.delete(2, 2);
System.out.println("String after deletion: "+sb);
}
}
Output:
Example 3: Removing first and last character from String
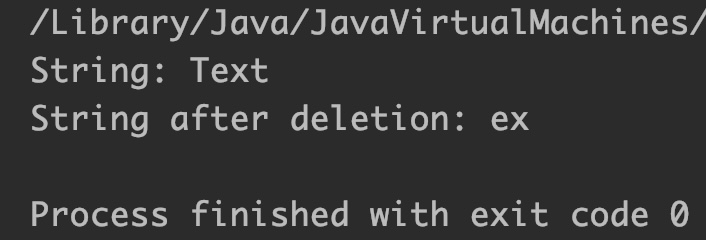
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Text");
System.out.println("String: "+sb);
//removing first character
sb = sb.delete(0, 1);
//removing last character
sb = sb.delete(sb.length()-1, sb.length());
System.out.println("String after deletion: "+sb);
}
}
Output:
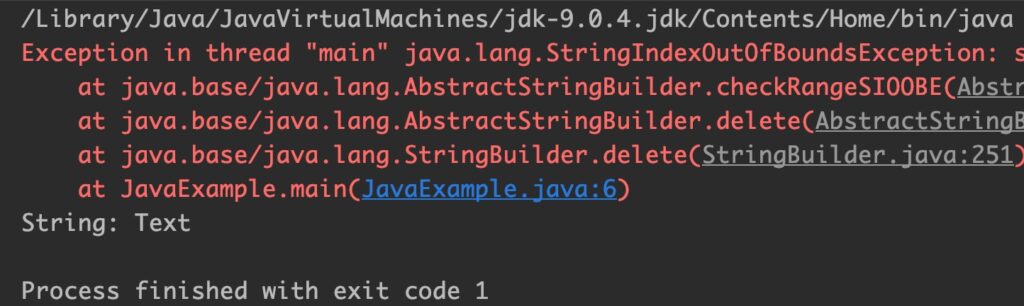
Example 4: When start index is greater than end index
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Text");
System.out.println("String: "+sb);
//start index is greater than end index
sb = sb.delete(2, 1);
System.out.println("String after deletion: "+sb);
}
}
Output: