Java StringBuffer insert() method is used to insert the given element at the specified position in this character sequence.
Syntax of insert() method
//insert string "hello" at the position (index) 1 sb.insert(1, "hello"); //insert integer 100 at the index 2 sb.insert(2, 100); //insert boolean 'true' at the end of StringBuffer instance sb.insert(sb.length(), true);
Here, sb is an object of StringBuffer class.
insert() Description
public StringBuffer insert(int offset, String str): It inserts the string str at the specified index offset. Similarly, there are multiple variations of this insert method that allow insertion of various data types into a StringBuffer instance. These variations are:
public StringBuffer insert(int offset, int i) public StringBuffer insert(int offset, long l) public StringBuffer insert(int offset, double d) public StringBuffer insert(int offset, float f) public StringBuffer insert(int offset, char ch) public StringBuffer insert(int offset, boolean b) public StringBuffer insert(int offset, char[] str) public StringBuffer insert(int index, char[] str, int offset, int length) public StringBuffer insert(int offset, Object obj) public StringBuffer insert(int offset, String str) public StringBuffer insert(int dstOffset, CharSequence cs) public StringBuffer insert(int dstOffset, CharSequence cs, int start, int end)
This method throws IndexOutOfBoundsException and StringOutOfBoundsException, if specified offsets are invalid.
insert() Parameters
The insert() method Parameters are:
- offset: It represents the index where the specified data needs to be inserted.
- start: It represents the start of the substring that needs to be inserted. (See example below)
- end: It represents the end of the substring that needs to be inserted.
- i, l, d, f, ch, b: Represents the values of data types that needs to inserted using insert() method.
- str: String that is inserted in the given StringBuffer character sequence.
insert() Return Value
- It returns a new StringBuffer object after insertion.
Example 1: Inserting int, long, float, double, char and boolean
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("Welcome");
sb.insert(sb.length(), 100);//inserting int
System.out.println(sb);
StringBuffer sb2 = new StringBuffer("Welcome");
sb2.insert(0, false); //inserting boolean at start
System.out.println(sb2);
StringBuffer sb3 = new StringBuffer("Welcome");
sb3.insert(sb3.length(), 5.25f); //inserting float at end
System.out.println(sb3);
StringBuffer sb4 = new StringBuffer("Welcome");
sb4.insert(sb4.length(), 6555.45); //inserting double
System.out.println(sb4);
StringBuffer sb5 = new StringBuffer("Welcome");
sb5.insert(0, 400L); //inserting long
System.out.println(sb5);
StringBuffer sb6 = new StringBuffer("Welcome");
sb6.insert(sb6.length(), 'X'); //inserting char
System.out.println(sb6);
}
}
Output:

Example 2: Insert char array at a specific position
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
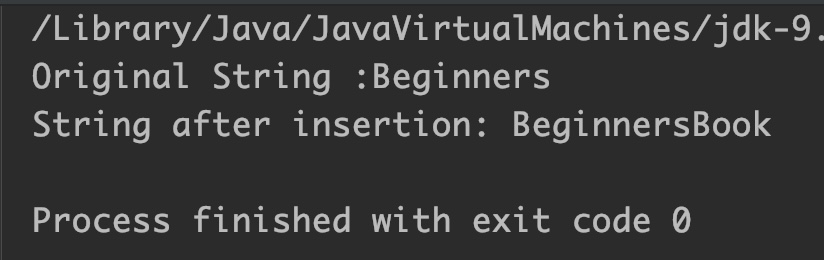
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("Beginners");
System.out.println("Original String :"+sb);
char[] chArray = {'B','o','o','k'};
// inserting char array at the end of sequence
sb.insert(sb.length(),chArray);
System.out.println("String after insertion: " + sb);
}
}
Output:
Example 3: Insert subsequence at a specific position
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
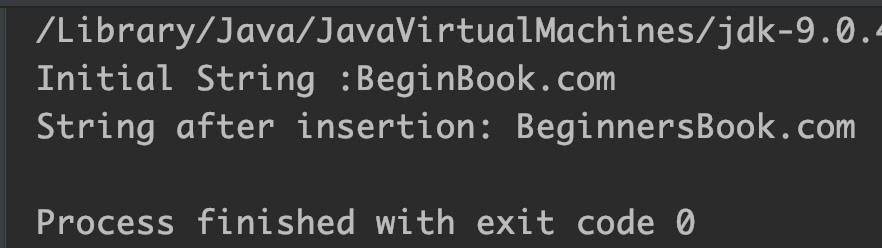
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("BeginBook.com");
System.out.println("Initial String :"+sb);
CharSequence cs = "Learners";
//inserting only a part of char sequence
//start and end specifies the part of char sequence
sb.insert(5,cs,4,8);
System.out.println("String after insertion: " + sb);
}
}
Output:
Example 4: StringBuffer insert(int offset, String str)
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("Welcome BeginnersBook.com");
System.out.println("Given String :"+sb);
//insert string "to " at index 8
sb.insert(8, "to ");
System.out.println("String after insertion: " + sb);
}
}
Output:

Example 5: StringBuffer insert(int offset, Object obj)
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("Text");
System.out.println("Initial String :"+sb);
Object obj = "MyStringObj";//string object
Object obj2 = 400L; //long object
Object obj3 = 1.5f; //float object
//insert All three objects at the end of given string
sb.insert(sb.length(), obj);
sb.insert(sb.length(), obj2);
sb.insert(sb.length(), obj3);
System.out.println("String after insertion: " + sb);
}
}
Output:
