Format specifier in C is a String, starting with ‘%’ symbol that specifies the type of data that is being printed using printf() or read using scanf().
For example: In the following statement the %d is a format specifier that specifies that the data type of the variable num is int.
printf("%d", num);Format Specifier
| Specifier | Description |
|---|---|
| %c | It is used for unsigned character |
| %s | It is used for strings |
| %d | It is used for signed integer, which means it can hold positive as well as negative integers. |
| %f | It is used for floating point values such as 16.5, 19.67 etc. |
| %Lf | long double |
| %hi | signed short |
| %hu | unsigned short |
| %i | a decimal integer (detects the base automatically) |
| %o | Used for octal numbers |
| %x | Used for hexadecimal integer |
| %p | an address (or pointer) |
| %u | int unsigned decimal |
| %e | a floating point number in scientific notation. It is also known as Mantissa or Exponent. |
| %E | same as %e |
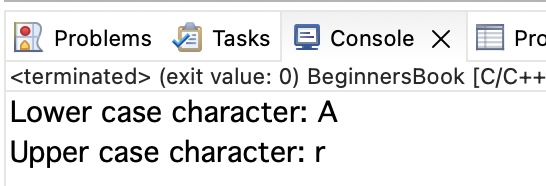
Example 1: Character format specifier %c
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char ch = 'A';
char ch2 = 'r';
printf("Lower case character: %c",ch);
printf("\nUpper case character: %c",ch2);
return 0;
}Output:
Example 2: String format specifier %s
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char str[20];
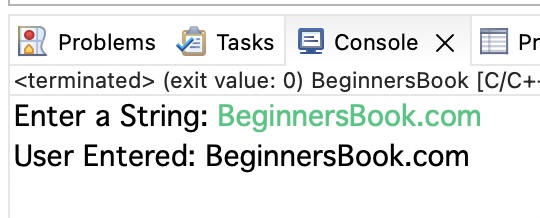
printf("Enter a String: ");
scanf("%s", str);
printf("User Entered: %s", str);
return 0;
}Output:
Example 3: Integer format specifier %d
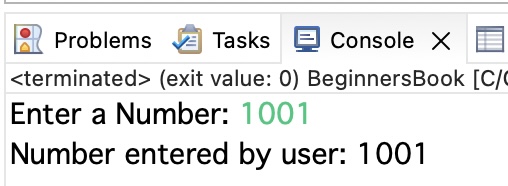
Here, we are taking the input from the user and displaying the same number as output. User is asked to enter an integer number so are using %d specifier. The same %d specifier is used while printing the input number.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int number;
printf("Enter a Number: ");
//%d format specifier for integer
scanf("%d", &number);
printf("Number entered by user: %d", number);
return 0;
}Output:
Example 4: Float format specifier %f
To print the number value with the decimal points, we are using %f format specifier.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
float number =15.55;
printf("%f",number);
return 0;
}Output:
15.550000
Example 5: Octal format specifier %o
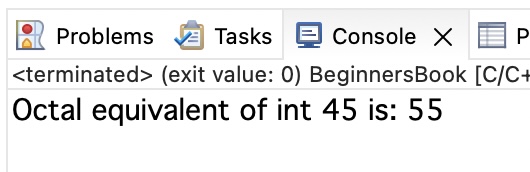
Here we are using octal format specifier %o to convert a decimal value to an octal value. In the following example, we just used the format specifier %o to print the octal equivalent value of the given decimal number.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int num = 45;
printf("Octal equivalent of int %d is: %o", num, num);
return 0;
}Output:
Example 6: Hexadecimal format specifier %x
This is similar to the example above. In this example, we are using format specifier %x to print the hexadecimal value of the given decimal number.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int num = 45;
printf("Hexadecimal equivalent of int %d is: %x", num, num);
return 0;
}Output:
