Data type specifies which type of data can be stored in a variable. For example, an int variable store integer value, char variable store characters, float variable store float value etc. These int, char and float keywords are data types that basically defines the type of data. In this guide, you will learn about data types in C language with examples.
The reason why we specify the data type of variable while declaring it, so that compiler know which type of data this variable can accept.
Types of Data Types in C
1. Primary data type
2. Derived data type: Array, pointers, struct, and union are the derived data types in C. We will discuss these in separate tutorials.
3. Enumerated data type: User defined data type, declared using enum keyword.
4. Void data type: Mostly used as a return type of function that does not return anything.
5. Boolean data type: Represents variables that can store either true or false. Represented by bool keyword.
Primary Data type in C
The following 5 data types in C are known as primary data types:
1. int: The int data type is used for integer values such as 5, 86, 99, 1002 etc.
2. char: The char data type is used for character values such as ‘A’, ‘p’, ‘u’, ‘M’ etc.
3. float: The float data type is used for decimal points values or real values such as 5.5, 10.91 etc.
4. double: The large floating point values are stored in double variables.
5. void: This is generally used as a return type of a function that does not return anything.
| Data Type | Memory Size | Range |
|---|---|---|
| int | 2 bytes | −32,768 to 32,767 |
| signed int | 2 bytes | −32,768 to 32,767 |
| unsigned int | 2 bytes | 0 to 65,535 |
| short int | 2 bytes | −32,768 to 32,767 |
| signed short int | 2 bytes | −32,768 to 32,767 |
| unsigned short int | 2 bytes | 0 to 65,535 |
| long int | 4 bytes | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
| signed long int | 4 bytes | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
| unsigned long int | 4 bytes | 0 to 4,294,967,295 |
| char | 1 byte | -128 to 127 |
| signed char | 1 byte | -128 to 127 |
| unsigned char | 1 byte | 0 to 255 |
| float | 4 bytes | 3.4E-38 to 3.4E+38 |
| double | 8 bytes | 1.7E-308 to 1.7E+308 |
| long double | 10 bytes | 3.4E-4932 to 1.1E+4932 |
Data Type in C Example
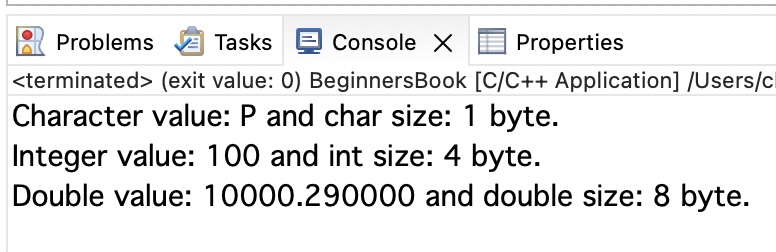
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int num = 100;
char ch = 'P';
double bigNum = 10000.29;
printf("Character value: %c and char size: %lu byte.\n",
ch, sizeof(char));
printf("Integer value: %d and int size: %lu byte.\n",
num, sizeof(int));
printf("Double value: %lf and double size: %lu byte.\n",
bigNum, sizeof(double));
return 0;
}Output: