In this guide, you will learn array of structures in C. An array of structures is an array with structure as elements.
An int array stores the elements of int type. Similarly an array of structures store the structures of same type as elements.
For example:
Here, stu[5] is an array of structures. This array has 5 elements and these elements are structures of the same type “student”. The element s[0] will store the values such as name, rollNum, address & marks of a student, similarly element s[1] will store these details for another student and so on.
struct student {
char name[60];
int rollNum;
char address[60];
float marks;
} stu[5];
This can be represented as a diagram like this:
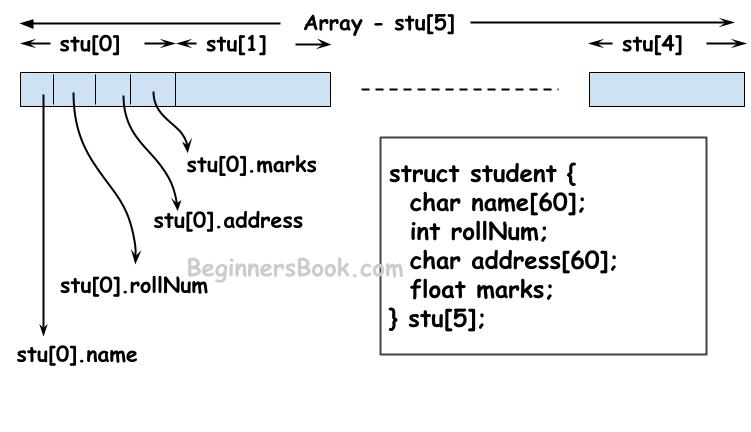
Example: Array of structures in C
In this example, we have an array of structures. The array is represented by s. The s[5] means that the array can hold 5 elements. These elements are student structure. This means that s[0] stores the details of first student, s[1] stores the details of second student and so on.
#include <stdio.h>
struct student {
char name[60];
int rollNum;
char address[60];
float marks;
} s[5];
int main() {
int i;
printf("Enter student information:\n");
// getting information
for (i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
s[i].rollNum = i + 1;
printf("\nFor roll number%d: \n", s[i].rollNum);
printf("Enter Name: ");
scanf("%s", s[i].name);
printf("Enter Address: ");
scanf("%s", s[i].address);
printf("Enter marks: ");
scanf("%f", &s[i].marks);
}
printf("\nPrint student Information:\n");
// printing information
for (i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
printf("\nRoll number: %d\n", i + 1);
printf("First name: ");
puts(s[i].name);
printf("Address: ");
puts(s[i].address);
printf("Marks: %.1f", s[i].marks);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}Output:
Enter student information: For roll number1: Enter Name: Tommy Enter Address: Delhi Enter marks: 99 For roll number2: Enter Name: Steve Enter Address: Noida Enter marks: 86.5 For roll number3: Enter Name: Hari Enter Address: Agra Enter marks: 88.9 For roll number4: Enter Name: Ajeet Enter Address: Delhi Enter marks: 99.5 For roll number5: Enter Name: Smith Enter Address: Chennai Enter marks: 91.5 Print student Information: Roll number: 1 First name: Tommy Address: Delhi Marks: 99.0 Roll number: 2 First name: Steve Address: Noida Marks: 86.5 Roll number: 3 First name: Hari Address: Agra Marks: 88.9 Roll number: 4 First name: Ajeet Address: Delhi Marks: 99.5 Roll number: 5 First name: Smith Address: Chennai Marks: 91.5