Arithmetic operators are used to perform arithmetic operations on the operands. For example, x + y is an addition arithmetic operation, where x and y are operands and + symbol is an arithmetic operator. C supports following arithmetic operators:
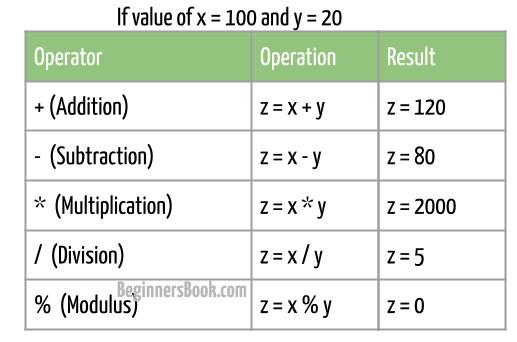
1. Addition(+) Operator Example
It adds two operands. In the following example, we have two integer variables and we are finding the sum of these numbers using + operator.
#include <stdio.h>
int main ()
{
int x = 100, y =20;
int sum;
//Addition(+) operator
//The addition result is stored in variable sum
sum = x+y;
//print result
printf("Sum of %d and %d is: %d",x, y, sum);
return 0;
}
Output:
Sum of 100 and 20 is: 120
2. Subtraction(-) Operator Example
The – operator is used for subtraction. Here, we are subtracting the value of y from the value of x. The subtraction result is stored in an int variable, which is displayed using printf() at the end of the program.
#include <stdio.h>
int main ()
{
int x = 100, y =20;
int sub;
//Subtraction(-) operator
//The result is stored in "sub"
sub = x-y;
//print subtraction result
printf("x - y is: %d", sub);
return 0;
}
Output:
x - y is: 80
3. Multiplication(*) Operator Example
The * operator is used for multiplication. It multiplies two operands as shown in the following program.
#include <stdio.h>
int main ()
{
int x = 100, y =20;
int product;
//Multiplication(*) operator
product = x*y;
//print multiplication result
printf("Multiplication of %d and %d is: %d", x, y, product);
return 0;
}
Output:
Multiplication of 100 and 20 is: 2000
4. Division(/) Operator Example
The / operator, returns the quotient value after dividing left-side operand by right-side operand. For example, if 10 is divided by 5, then the / operator would return 2 (quotient).
#include <stdio.h>
int main ()
{
int x = 100, y =20;
int quotient;
//Division(/) operator, it returns the quotient after
//dividing x by y
quotient = x / y;
//print Division result
printf("Quotient value after dividing %d by %d is: %d", x, y, quotient);
return 0;
}
Output:
Quotient value after dividing 100 by 20 is: 5
5. Modulus(%) Operator Example
The % operator returns the remainder after dividing the left-side operand by right-side operand. For example, 10 % 2 would return 0 as 10 is perfectly divisible by 2.
#include <stdio.h>
int main ()
{
int x = 100, y =20;
int rem;
//Modulus(%) operator, it returns the remainder after
//dividing x by y
rem = x % y;
//print Modulus result
printf("Remainder value after dividing %d by %d is: %d", x, y, rem);
return 0;
}
Output:
Remainder value after dividing 100 by 20 is: 0