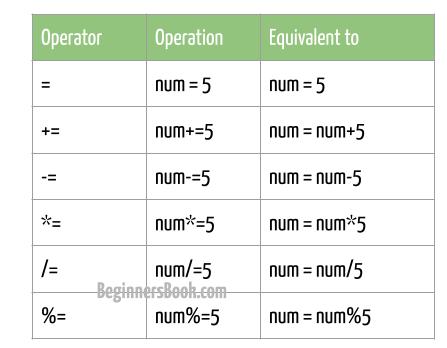
Assignment operators are used to assign value to a variable. The left side of an assignment operator is a variable and on the right side, there is a value, variable, or an expression. It computes the outcome of the right side and assign the output to the variable present on the left side. C supports following Assignment operators:
1. Simple Assignment = Operator Example
This is one of the simplest assignment operator, it simply assigns the right side value to the left side operand.
#include <stdio.h>
int main ()
{
int n; //integer variable
char ch; //character variable
float f; //float variable
// Simple assignment operator to assign values to variables
n = 1;
ch = 'A';
f = 15.565f;
// Displaying the values of all the variables
printf("The value assigned to 'n': %d", n);
printf("\nThe value assigned to 'ch': %c ", ch);
printf("\nThe value assigned to 'f': %f ", f);
return 0;
}
Output:

2. += Operator Example
The += assignment operator is a combination of + arithmetic operator and = simple assignment operator. For example, x += y; is equivalent to x = x+y;.
It adds the right side value to the value of left side operand and assign the result back to the left-hand side operand.
#include <stdio.h>
int main ()
{
int x = 100, y = 20, z = 50;
// += Operator demonstration
x += 10;
y += 10;
z += 10;
//Display values after += operations
printf("Value of variable x: %d", x);
printf("\nValue of variable y: %d", y);
printf("\nValue of variable z: %d", z);
return 0;
}
Output:
Value of variable x: 110 Value of variable y: 30 Value of variable z: 60
3. -= Operator Example
The -= assignment operator is a combination of – and = operators. It subtracts the right side value from the left side value and assign the result to left side operand. For example, x -= y; is equivalent to x = x-y;.
#include <stdio.h>
int main ()
{
int x = 100, y = 20, z = 50;
// -= Operator demonstration
x -= 50;
y -= 10;
z -= 5;
//Print variable's values after -= operations
printf("Value of variable x: %d", x);
printf("\nValue of variable y: %d", y);
printf("\nValue of variable z: %d", z);
return 0;
}
Output:
Value of variable x: 50 Value of variable y: 10 Value of variable z: 45
4. *= Operator Example
The *= assignment operator is a combination of * and = operators. It multiplies the right side value to the left side value and assign the product of these numbers to the left side variable. For example, x *= y; is equivalent to x = x*y;.
#include <stdio.h>
int main ()
{
int x = 100, y = 20, z = 50;
// *= Operator to multiply the value of left operand
// by the value of right operand
x *= 2;
y *= 10;
z *= 1;
//Displaying values after *= assignment operations
printf("Value of variable x: %d", x);
printf("\nValue of variable y: %d", y);
printf("\nValue of variable z: %d", z);
return 0;
}
Output:
Value of variable x: 200 Value of variable y: 200 Value of variable z: 50
5. /= Operator Example
The /= assignment operator is a combination of / and = operators. It divides the left side operand by the right side operand and assign the quotient value of this division to the left side variable. For example, x /= y; is equivalent to x = x / y;.
#include <stdio.h>
int main ()
{
int num1 = 100, num2 = 50, div;
// The / operator returns the quotient value
div = num1 / num2;
printf("Value of num1: %d", num1);
printf("\nValue of num2: %d", num2);
printf("\nValue of num1 / num2 is: %d", div);
return 0;
}
Output:

6. %= Operator Example
The %= assignment operator is a combination of % and = operators. It divides the left side operand by the right side operand and assign the remainder value to the left side variable. For example, x %= y; is equivalent to x = x % y;.
#include <stdio.h>
int main ()
{
int num1 = 100, num2 = 50, mod;
// The Modulus % operator returns the remainder after division
mod = num1 % num2;
printf("Value of num1: %d", num1);
printf("\nValue of num2: %d", num2);
printf("\nRemainder after dividing num1 by num2 is: %d", mod);
return 0;
}
Output:
