In this guide, you will learn about instance and schema in DBMS.
DBMS Schema
Definition of schema: Design of a database is called the schema. For example: An employee table in database exists with the following attributes:
EMP_NAME EMP_ID EMP_ADDRESS EMP_CONTACT -------- ------ ----------- -----------
This is the schema of the employee table. Schema defines the attributes of tables in the database. Schema is of three types: Physical schema, logical schema and view schema.
- Schema represents the logical view of the database. It helps you understand what data needs to go where.
- Schema can be represented by a diagram as shown below.
- Schema helps the database users to understand the relationship between data. This helps in efficiently performing operations on database such as insert, update, delete, search etc.
In the following diagram, we have a schema that shows the relationship between three tables: Course, Student and Section. The diagram only shows the design of the database, it doesn’t show the data present in those tables. Schema is only a structural view(design) of a database as shown in the diagram below.
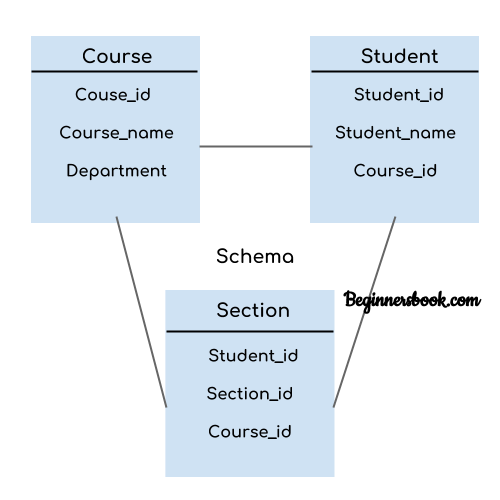
The design of a database at physical level is called physical schema, how the data stored in blocks of storage is described at this level.
Design of database at logical level is called logical schema, programmers and database administrators work at this level, at this level data can be described as certain types of data records gets stored in data structures, however the internal details such as implementation of data structure is hidden at this level (available at physical level).
Design of database at view level is called view schema. This generally describes end user interaction with database systems.
To learn more about these schemas, refer 3 level data abstraction architecture.
DBMS Instance
Definition of instance: The data stored in database at a particular moment of time is called instance of database. Database schema defines the attributes in tables that belong to a particular database. The value of these attributes at a moment of time is called the instance of that database.
For example, we have seen the schema of table “employee” above. Let’s see the table with the data now. At this moment the table contains two rows (records). This is the the current instance of the table “employee” because this is the data that is stored in this table at this particular moment of time.
EMP_NAME EMP_ID EMP_ADDRESS EMP_CONTACT ------- ------ ----------- ----------- Chaitanya 101 Noida 95******** Ajeet 102 Delhi 99********
Let’s take another example: Let’s say we have a single table student in the database, today the table has 100 records, so today the instance of the database has 100 records. We are going to add another 100 records in this table by tomorrow so the instance of database tomorrow will have 200 records in table. In short, at a particular moment the data stored in database is called the instance, this changes over time as and when we add, delete or update data in the database.
Leave a Reply